How to measure the width of a rim
Dimensions and parameters of car wheels
The selection of car wheels should be treated with great care and attention! Each disk has several parameters for installation on a car, each of which must be taken into account when choosing. Some parameters are unchanged, while others can be adjusted within a small range. This article will tell you about all the intricacies of choosing cast and forged wheels.
Disk options
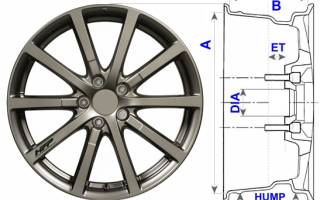
Size A (rim diameter in inches) – seat diameter – the diameter of the annular part of the rim on which the tire rests.
Dimension B (rim width in inches) - rim seat width - the distance between the inner surfaces of the wheel flanges. Determines the possible profile width of the installed tire. A deviation of 0.5-1 inch in the seat width is allowed, but for low-profile tires it should be minimal.
HUMP ( width in inches) – an annular protrusion, used for additional fixation when installing tubeless tire beads.
ET (offset in mm) – offset (offset) of the disk, i.e. a parameter that determines how deep the wheel is recessed into the car arch. The offset is the distance from the plane of the disk adjacent to the car hub to the plane passing through the axial middle of the width of the disk rim. For each vehicle, the manufacturer provides a list of acceptable wheel installation options. This parameter can be changed by +/- 5 mm without harm to the car's suspension. If the deviation is large, it is necessary to try on the disc on both the front and rear axles of the car, since it is possible that the disc will rest against suspension elements, fender liners or parts of the car’s brake system. In addition, installing wheels with an offset that is significantly less than intended leads to a significant decrease in vehicle stability in corners, increased steering sensitivity to road irregularities and uneven braking forces.
PCD – the number of mounting holes and the diameter of the circle of the centers of these holes. This value must correspond to the standard value, otherwise it is impossible to achieve reliable fixation of the wheel on the car hub. A deviation of even 1-2 mm can lead to misalignment of the wheel and fastening elements.
DIA (CO in mm) – diameter of the central hole of the disk. It must match the diameter of the centering protrusion on the vehicle hub. An upward deviation of its value is allowed. In this case, adapter centering rings are used to install the wheel.
Disk parameters can be indicated as follows, for example:
6×15 ET45 5×100 D57.1
6 – rim width in inches;
15 – disc diameter in inches
ET45 – disc offset (in mm);
5×100 – PCD , the number of mounting holes at a certain diameter location. It must be taken into account that for each car it (diameter) is different and cannot be changed under any circumstances;
D57.1 – DIA (TsO) diameter of the central hole of the disk, measured in mm;
6.5 J 15 H2 5×114.3 ET45 D54.1
6.5 – rim width in inches;
15 – disk diameter in inches;
5×114.3 – PCD , number of mounting holes at a certain diameter location.;
ET45 — disc offset (removal) (in mm);
D54.1 – DIA (TsO) diameter of the central hole of the disk, measured in mm;
J and H2 are symbols needed more by specialists. J encrypts information about the design of the rim flanges (can be JJ, JK, K or L) . And H2 is the design code for humps, ring protrusions on the rim flanges that serve to reliably hold the tubeless tire on the rim (there are many variations: H, FH, AH, etc.);
How to find out your rim size
The correct choice of wheel rims depends on the technical characteristics indicating all the parameters, namely width, diameter, offset, as well as DIA (hub mounting diameter) and PCD (drilling parameters).
You also need to know the marking designation. It indicates the standard parameters of any type of wheel products:
Markings are indicated on the inside. Typically, manufacturers duplicate them in accompanying documents and on packaging if the product is new.
Disk options
To determine what the marking means, you need to know the width and diameter of the wheel product.
Drilling or bolting
This is one of the most difficult parameters to study, indicating the diameter of the mounting bolts. Drilling is measured from the center area of the stud to the opposite area where the element is located on the wheel.
Quite often, manufacturers indicate the disc bolt pattern parameters using shot depending on the number of holes for fastening.
Let's assume the figures are 6/222.25. The first number shows the number of drillings for fastening the bolts, and the second number indicates the drilling in millimeters.
Disc offset
This indicator is marked with the English letters ET. What is ET in disks and why is it needed? The indicator indicates the distance from the plane of the wheel product to the middle zone of the rim. The mating surface of the wheel product indicates the pressing plane of the disk to the hub.
Departure parameters can be:
- with zero indicator;
- with negative;
- with positive.
Zero offset indicates that the plane of the disc corresponds to its middle zone. Thus, the lower the indicator, the more the wheel product protrudes from the outside of the car. If the overhang indicator is increased, this means that the disc is deeper into the interior of the car.
It is also necessary to take into account the fact that depending on the width of the product, the overhang indicators differ. Manufacturers indicate in the documentation accompanying the vehicle a smaller offset value for wheels with a large width.
Diameter and other parameters of the disk schematically
What is HUMP(H)?
The hump is the protrusion of a ring on a disc rim. This element is used as protection against car tires coming off. Usually 2 humps (H2) are used for a wheel.
In some cases, a hump may not be used or only one may be used, depending on the vehicle configuration. Types of Humps:
- combined (CH);
- flat (FH);
- asymmetrical (AH).
PCD Disc Parameters
The PCD value refers to the diameter of the circle of the center holes on the wheel rim. That is, this is the diameter of the holes for fastening the bolts.
DIA drive option
The DIA parameter indicates the diameter of the hole located in the center of the disk. Casting manufacturers prefer to create a large DIA center hole diameter. This is done to ensure that the wheels are applicable and universal for all types of cars.
Despite the fact that the size of the hub may differ depending on the vehicle model, the auto disk is installed using an adapter ring or bushing.
Marking
As an example, consider the markings of the 9J x20H PCD 5×130 ET60 DIA 71.60 wheel rim:
- The number 9 indicates the width, measured in inches. To convert inches to centimes, the total figure is multiplied by 25.4.
- The letter J indicates the design elements: the shape of the disc flanges. This parameter does not play an important role in the selection.
- The letter X denotes the indivisibility of the disc.
- The number 20 indicates the landing diameter of the wheel product. This indicator corresponds to the fit of a car tire.
- The letter H denotes the presence of one hump or ridge on the rim.
- The abbreviation is PCD 5×130, where the number 5 indicates the number of drillings for fastening the nuts or bolts and the number 130 indicates their PCD diameter in millimeters.
- The ET60 marking indicates disc offset. In this situation the figure is 60 mm.
- The DIA value 71.60 indicates the diameter of the center drill. Typically, DIA corresponds to the fit of the hub and is indicated in millimeters. If the DIA is greater than the hub diameter, then a centering ring is used to install the disc.
The following information is also included with the label:
ISO, SAE, TUV - these abbreviations indicate the organizations that tested the wheel product, similar to the Russian GOST. The standards that correspond to the wheel marking are also indicated.
Maxload indicates the permissible load on a car wheel. This indicator is indicated in kilograms and pounds.
What does parameter 700c mean?
This designation is used for large types of wheels on SUVs and Nivas. According to the accepted ISO classification, this figure is 29 inches. Typically 700c wheels are used for off-road racing.
Due to the use of 29 inch wheels:
- management indicators are improved;
- braking distance on unpaved surfaces is reduced and aerodynamics is increased;
- the vehicle's cross-country ability on soft soils and sand increases;
- it becomes possible to install powerful brakes.
To select wheels that match a particular type of car, it is recommended to determine the diameter of the wheel and analyze the markings indicated on the rim. Also, do not forget that safe driving ultimately depends on this element.
Wheel rim width - what is it, what does it affect?
Cars are equipped with wheels of different widths. The difference depends on the design features of the vehicle and its operational characteristics. One of the important parameters is the width of the disk. If you choose this size incorrectly, neglecting the factory recommendations, the car will not be able to provide full functionality. How the disk width parameter is designated, how it is measured and how it affects the operation of the machine, we will talk about this further.
How is the width of a wheel rim indicated?
The width of the rim is indicated in the rim parameters line. For example, let’s take a look at the wheel markings from the VAZ-2110, which are designated as follows: 5Jx14/ET35/4×98/DIA 58.6. The first number is 5, this is the size of the rim width. Distance is measured in inches. To convert it to centimeters, you need to multiply the value by 2.54 cm. In our case: 5 x 2.54 = 12.7 cm. This is the distance between the inner edges.
The letter “J”, which is located behind the 5th, is the type/shape of the rim flange and has nothing to do with the width.
The most common rims are available in widths from 5 to 10 inches. And the most common type of flange is “J” or “JJ” (SUVs). The marking is applied to the rim itself: for steel “stampings” on the outside, and for light-alloy wheels – inside the cavities of the spokes. To avoid cleaning a dirty wheel, the parameters can be found in the car’s operating instructions. Also, the automaker places information plates on the car body with dimensions that can most often be found in places such as:
- glove box (glove compartment);
- reverse side of the fuel filler flap;
- driver's door pillar.
If you install wider wheels, you will have to buy wider tires. A moderate sizing error, just 1-1.5 inches larger, will give the vehicle better directional stability. If you install the rims much wider, the tires will begin to touch the wheel arch and fender arch.
A narrower rim width than recommended by the manufacturer reduces the vehicle's directional stability. The car will start to “float” on the road because the tires will be too big for the rim. If you select tires for wheels in accordance with the rules, then it is recommended to install wheels a little narrower in the winter, and wider in the summer.
How does rim width relate to offset?
If you still want to install wide wheels and prevent the tires from touching the body niches, then you should also change the disc offset. This is another parameter, which in our VAZ example is indicated as “ET35”. Disk offset is the distance from the mating plane of the disk core to its vertical axis, measured in cm. Overhang can be:
The smaller the offset distance number, the more the wheel is pushed outward from the wheel arch of the car.
In the vast majority, discs are produced with a positive offset. Let's look at an example: you want to install 7-inch wheels instead of 5-inch VAZ rims. This means that it is necessary to slightly change the “ET” size in order to prevent the tire from shuffling on the locker. Consequently, it is necessary to select wheels with a smaller offset than 35 cm. Thus, it is possible to eliminate wheel contact and leave the load arm on the suspension unchanged. In some cases, wider discs can be installed with standard “ET”, but then it is recommended to adjust the distance with spacers to increase the offset.
The wheel width must correspond to the factory settings. But if you want to play around with size a little, then take into account an additional parameter - the “ET” offset. Even a slight displacement of the load arm on the suspension significantly accelerates the wear of wheel bearings and tires.
How to repair a tire yourself
How to remove and install wheel covers
Tire repair kit: when it comes in handy, composition, how to use
The difference between a tube tire and a tubeless tire - what is the difference?
Differences between radial and bias tires - design features
Discs with beadlocks - what are they: design features
Maximum load on a wheel rim - what is it, where is it written, how to calculate?
Wheel storage covers: types and selection rules
How to replace a wheel yourself
How to choose wheels for a car? What parameters need to be taken into account?
Which wheels are better in summer?
Disk DIA - what is it?
Mixed-width wheels - what are they? Why install?
Forged wheels - features. Is it worth taking?
PCD disk - what is it?
Alloy wheels - types and selection rules
What is wheel bolt pattern and how to measure it
One of the main parameters of wheel rims is the number of mounting holes and their location relative to the wheel axis. The English term PCD, in domestic auto slang called a bolt pattern, contains information about the number of studs or bolts, as well as the diameter of the circle in which their centers are inscribed.
For example, a typical size for VAZ cars will be designated as PCD 4 x 98 .
5 main wheel sizes
The most common wheels are found, except for those that came from old FIAT models and some other cars, VAZ PCD 4 x 98 , with 4 and 5 bolts (studs).
The most popular bolt patterns:
Although it is difficult to judge the actual prevalence of specific sizes, there are many others used on fairly well-known mass-produced cars.
Naturally, the disc parameters are not limited by the size of the bolt pattern.
There are others, no less important:
- diameter of the central hole;
- width;
- departure;
- disc edge parameters and much more.
How to measure the bolt pattern of a disc yourself
In fact, the need for measuring procedures rarely arises. The required parameter can be easily found out from the characteristics of a particular machine, and for any disk it is indicated on the product labeling.
But the designation of a used part may have been destroyed, so you will have to determine the bolt pattern using a ruler.
Measurements should be made with the greatest possible accuracy. It is very difficult, for example, to distinguish a 4x98 disk from a 4x100 one. It often happens that VAZ cars are driven with enlarged PCD rims, which is wrong and very dangerous.
Even if the wheel is centered more or less normally and does not bounce while driving, the lack of complete contact between the chamfers of the fastening bolts and the disk sockets causes high stress in the metal, wear of the holes, fatigue in the wheel bolts and a high probability of losing the wheel while driving.
There are two measurement methods - for an even number of studs and universal.
If the number is even, it is enough to mark the centers of the holes with the greatest possible accuracy and determine the distance between these centers for diametrically opposite bolts.
You will have to use a caliper; a regular ruler will give too much error. For example, on a disk you need to take the size between the edges of the holes, one from the inside, the other from the outside. Since the diameters of the bolt sockets are made with high precision, this will be the desired PCD.
Calculation formula and compatibility tables
If there are an odd number of holes, one measurement will not work. In this case, you need to measure the distance between the axes of two adjacent bolts, and then apply simple formulas for calculations.
Let's say the distance is equal to some number X. Then, depending on the number of bolts from 3 to 5, the following formulas are used:
- 3 bolts. PCD=1.155*X
- 4 bolts. PCD=1.414*X
- 5 bolts. PCD=1.701*X
The formulas are obtained as a result of simple geometric manipulations; everyone can personally check and obtain more accurate coefficients.
As approximate reference information, you can use the table of compatibility of car models based on the same PCD.
As mentioned above, this cannot in any way mean complete interchangeability of disks, since all their other parameters rarely coincide.
It should be borne in mind that the wheels that were equipped with the cars could differ greatly depending on the specific modification of the model and the equipment ordered.
How to find out the bolt pattern of a disk
When purchasing a set of wheels for a car, a number of parameters are taken into account, of which the bolt pattern is important. It is understood as a set of characteristics for choosing a kit for a specific car. You can measure them yourself using a number of tools; in addition, selection is possible using compatibility tables.
Size indicators
When purchasing a car, especially the first one, the owner rarely thinks about the fact that he should choose wheels carefully. Kits on the market often differ because they are designed for different cars, although there may not be any visible differences.
In order for the selection to be accurate and the wheels to fit the car, a number of sizes are taken into account. If there is an error in determining one of them, the disks will not be installed, but even if successful, operation of the machine will become unsafe. Before measuring the bolt pattern, you should understand what is included in it. Among the main sizes:
- number of holes for mounting the wheel (in the marking it is designated as LZ);
- distance between screw holes;
- the diameter of the circle along the edges of which holes for the bolts are made (in the disk marking it is designated as PCD);
- hub window indicator (you can find it out by the DIA number);
- degree of disc overhang (the ET marking is responsible for it).
Each of the characteristics is important when choosing a disk set. Their accounting becomes mandatory if wheels are purchased remotely - if they are incompatible, you will need to spend time communicating with the seller, returning the goods, or searching for a new set.
Passenger cars typically use 3-6 bolts per disc, which is much less than trucks. Given the diameter and weight of their wheels, each requires 12-15 bolts to secure.
Important! Domestic cars, especially Soviet-made ones, mostly have 4 bolts for installing disks. The Niva is an exception; its wheels use 5 bolts.
You can determine the exact number of fasteners needed to mount the wheels by looking at the stock wheels. By simple inspection it will become clear how many sockets are in the wheel and how many bolts are needed for them.
How to measure yourself
It’s possible to find out the bolt pattern yourself; this is possible with a ruler (preferably a caliper). They measure the distance between the windows, and the ruler has an error because it does not take into account the bend. You can take measurements in several ways, which are combined for greater accuracy.
Adjacent holes
This parameter is determined taking into account the indicator of the circle where the central part of the slot made for the mounting bolts is located. The diameter can be easily calculated using a ruler, although a compatibility table has been developed for popular cars. If a ruler is used, then the distance between adjacent bolts is measured in a straight line.
The resulting figure is multiplied by a coefficient determined by the number of holes in the disk. It should be said right away that the transverse circumference of VAZ cars is standardized at 98 mm, and in Niva it is 139.7 mm. The coefficients are as follows:
- 3 bolts - 1.155;
- 4 fasteners - the value for multiplication is 1.414;
- 5 — 1,701;
- 6 bolts - 2;
- 10 pins - 3.326.
Far windows
Instead of nearby holes, you can determine the bolt pattern even with a ruler with minimal error, using distant windows. The easiest way to measure wheels is if there is an even number of bolts - 4,6,8. The length of a straight line drawn between opposite holes will indicate the required value.
If there are 5 bolts on the disk, the distance between holes that are not adjacent is measured. The resulting figure is multiplied by a coefficient of 1.051, which gives the most accurate PCD result.
Hub window diameter
The hub center window size is specified in the bolt pattern charts and the complete bolt pattern formula mentioned below. Even if there is no ready-made information at hand, the results can be easily obtained with a ruler or a more accurate caliper. For example, the window diameter in the VAZ model 2110 is made at 58.6 mm.
In addition to the listed characteristics, disc offset is also important. It refers to the location of the vertical axes of symmetry of the wheel in relation to the point of alignment with the hub. The offset can be negative, as well as zero or positive, but even if the selection for it was unsuccessful, the disk can be installed. This is undesirable, because the car’s suspension will begin to function incorrectly and will greatly impair driving safety.
Bolt pattern formulas
To accurately determine whether the kit and car make are compatible, bolt pattern formulas are used that indicate the parameters of the disks. There are abbreviated and full values, but absolutely all parameters are indicated only in the latter.
This formula is used by disc manufacturers who apply the appropriate markings to their products. It looks like: 8Jx15 H2 4x100 ET0 D54.1 and for an inexperienced car owner it is a random set of numbers and letters. In fact, each parameter can be deciphered:
- 8 Jx15 - the first number indicates the width of the rim, the diameter being 15 inches. The X here represents the type of wheel, in this case they are cast or forged. The letter J indicates the possibility of using the wheel only on cars with single-wheel drive - rear or front, because all-wheel drive is designated as JJ.
- H2 - Displays the number of haps, which are otherwise called horse lugs. They hold tubeless tires on the rim and there are products with one hub or without it at all. These elements secure the tire, preventing it from depressurizing, and also help to corner more efficiently.
- 4x100 is a PCD indicator, the first digit in which reflects the number of bolt sockets, the second - the transverse diameter of the circle.
- ET0 - gives an understanding of the disc offset, in this case it is zero. If the number is 40, this is a positive offset, and the designation ET-40 shows a negative offset.
- D54.1 - this designation indicates the diameter of the hub window, the figure is given in millimeters.
The diameter and width of the wheel rim are indicated in inches, while other characteristics are reflected in millimeters.
Abbreviated
The abbreviated digital characteristic is simplified; it contains only two indicators. the 4x98 formula reflects that the wheel has 4 bolts located along a 100 mm circumference. This is the standard bolt pattern of the VAZ 2110; other cars also have circles from 100 to 139.7.
Before purchasing wheels, measure the hub. There may be no differences, for example, a disk with a 98-th circle will visually fit on a hub with a diameter of 100. In practice, such a disk will not fit tightly to the hub, the wheel will be skewed, and safety will be at risk.
Bolt tables
Calculating the bolt pattern is rarely used, because there are compatibility tables. The driver needs to find a table for a specific model and look at the parameters for it. They include all popular cars used in Russia.