What does offset on rims mean?
Disc ejection (ET) - what is it and what does it affect?
Offset is the most important geometric parameter of a wheel rim. And this is by no means an exaggeration. We will try to explain the reason for this, as they say, with our fingers. So, if a car wheel does not fit in diameter, number of holes for mounting bolts, or the interval between these holes, then it simply cannot be put on the hub. But usually such discrepancies with the standard (declared by the car manufacturer) offset are not very large, which makes installation possible without difficulties. Will the wheel fulfill its role one hundred percent in this case? And if not, then what will such an experiment lead to? On the Internet on thematic websites, vehicle owners often discuss the topic of how much the offset of the installed disc can differ from the recommended one, and if this discrepancy is acceptable, then in what direction? Often the points of view expressed have diametrically opposite directions.
As for the distributors of car wheels, be it a specialty store or a car market, in nine out of ten cases they will say that a small deviation of the offset from the standard parameters is acceptable. And they will certainly add that if the assembled wheel is easily mounted on the hub, without catching or touching either the body or the suspension during rotation, then it can be used without any doubts or risks. Moreover, people selling wheel spacers will assure that reducing the offset, regardless of the recommended parameters, is not a problem at all and does not pose any danger. All this is easily explained by their desire to quickly sell their goods, and often by banal ignorance. But how are things in reality? Let's start with the basics.
How to determine disc offset?
Disc offset is the distance from the central axis of the disc to the plane of attachment to the hub. Determining it is elementary, because there is a simple formula that looks like this:
ET=XY/2 (calculated in millimeters)
- ET – required value (offset).
- Y – width of the rim itself (total).
- X is the distance between the plane of application of the disk to the hub and its internal plane.
Obviously, the resulting number can be either with “+” (the most likely option), or with “-“, or even go to zero. An important point is the fact that offset directly determines the width of the wheelbase, since it forms the interval between the centers of the wheels located on the same axle. Analysis of the formula also shows that it is not affected by either the disc diameter, width, or tire dimensions.
Car suspension loads are calculated based solely on the force application arm, which is the distance from the hub to the center of the wheel.
This means that there can be only one wheel offset required for a particular car model. Regardless of the tire size and the size of the wheels themselves. The offset value is indicated on the surface of each disc. This is the ETxx marker, where xx is the distance in millimeters. It, as already mentioned, can be zero (ET0), positive (ET35) or negative (ET-35)
Are disc offset deviations allowed?
Regardless of how convincing the sellers' arguments are, you must clearly understand the fact that the offset of the disc you purchase must be 100% consistent with the vehicle manufacturer's instructions .
In no case are the slightest deviations in any direction allowed. It is very simple to explain such a categorical statement. Even with a tiny discrepancy in values, the operating conditions of absolutely all suspension elements without exception change automatically. In this case, forces arise for which these nodes are not designed. In addition, the vectors of application of these forces change, which is also not provided for by the chassis design. As a result, the service life of the mechanisms is significantly reduced, and when critical loads occur, the suspension units may completely collapse, which is very dangerous to life. Statements by CD sellers about a variety of options and nuances are just an attempt to sell you any product, in the absence of one that is ideally suited to your needs. Words about possible permissible deviations significantly expand the offered range of discs, and therefore increase the opportunity to earn money. No more.
Different configurations of one car model
Some car enthusiasts have noticed that different parts for different versions of the same car model are often used. This is due to the fact that when designing and calculating the parameters of components of each modification, a huge number of variables are taken into account, which can differ markedly for cars of the same line. An example of this is various power plants having different dimensions and weight. According to these calculations, taking into account in each case the acting forces and vectors of their application, the final suspension design is formed. This allows us to guarantee the client reliability, ride comfort, high-quality handling and other characteristics, with minimal production costs.
In the old days, most vehicle manufacturers manufactured parts in such a way as to provide a large margin of safety in the main structures of the car, including the suspension. Today, the trend in the market is such that there is a demand for reducing the cost of transport, which is achieved through more accurate calculations. This resulted in a decrease in the safety margin of most parts.
Forces acting on suspension elements
Absolutely any element of the suspension is subject to several multidirectional forces. And it is quite natural that this list increases with the complexity of the design, which is very different from modern machines. Therefore, we offer for consideration the simplest example, where the hub is attached to the body by means of a lever and a strut with a shock absorber (McPherson system).
The force exerted on the wheels is directed upward from the plane along which the car is moving, and the mass of the car is distributed between all wheels. In this case, the points of application of these forces are the centers of the tire contact patch area. And if we assume that the suspension and camber angles are in ideal condition, and the wheels are well balanced, then these centers will be located on the axis of symmetry of each wheel. It is in this place that the axis of the shock absorber strut should fall.
Everything else is simple. The acting force corresponds to the proportion of the car's mass attributable to the wheel. It is directed away from the ground and creates moments in the levers, wheel bearing, and struts with shock absorbers. In the first two cases it will be tension, and in the last case it will be compression. All these points are carefully calculated at the design and construction stage. Naturally, a safety margin is provided for each part, but it was already mentioned above that it is constantly decreasing due to the widespread desire to reduce production costs.
When the calculated offset changes, the forces change their magnitude and direction, because a decrease in offset expands the wheelbase, and an increase - narrows it. This entails a displacement of the steering axis and a change in the parameters of steering wheel rotation, moments of forces and vectors of their application. This aspect also negatively affects the wear resistance of tires, maneuverability and controllability of the vehicle. Taken together, all of these factors lead to the fact that the suspension is operated in a mode that was not intended by the automaker. The level of driving safety decreases, and the service life of most structural elements decreases sharply.
In conclusion, let's say the following. If a new wheel with an offset that does not coincide with the standard one easily fits on the hub of your car, this is not a reason to use it without fear. It cannot be said that the operation of vehicles in such equipment will be safe. Wheel spacers can be a solution, but only if the offset is greater than standard, and you were able to find suitable spacers, which is often very problematic.
About disc offset - permissible deviations
Reading time: 6 minutes
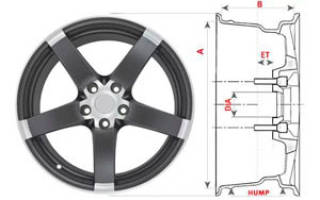
Quite often, car owners install new rims, and many do this not because of breakdown or wear of previous products, but in order to improve the appearance of their “iron horse”. So, when purchasing a new wheel, car enthusiasts always look not at its drilling, that is, the diameter of the mounting hole on the hub, the bolt pattern, or the number and length of the studs on which this wheel is installed, but few people pay attention to the offset of the product (ET), and this is very important indicator for normal operation of a wheel on a specific car model.
What is ET on rims? This question is asked by many car enthusiasts, especially those who purchased their cars relatively recently and, until today, have never encountered the problem of replacing wheels on them.
Geometric characteristics of the wheel rim
Disc ejection: what is it?
Disc offset, or ET indicator, is a dimensional parameter that is indicated on the rim of the product, regardless of its radius or material of manufacture (stamped, cast or forged), and indicates the distance from the mating plane of the wheel to the attachment point to the hub. This dimension is usually set by the car manufacturer.
ET offset on wheels: what is it and how does it affect the suspension and other parts in the car? Depending on the wheel offset, the load on the hub and the bending moment applied relative to it at the base of the suspension are distributed differently. Thus, each automobile concern dictates the strength limit for its parts, which determines the range of wheel offsets.
Some cars, especially when it comes to SUVs and sports cars, are equipped with additional plastic mud flaps, which determine the wheel offset, which in such cases can be zero or even negative, which gives the “iron horse” a very impressive look.
ET departure using 3 indicators as an example
ET on disks - what does it mean and how is it calculated
The designation in the form of two letters of the Latin alphabet ET is not accidental, since this value is international and is determined by the following formula and is expressed in mm, regardless of the country of the disk manufacturer:
Where X is the distance from the outer mating plane of the disk to its inner edge on the side of attachment to the hub or the size that is determined by measuring from the side edge of the wheel along the sides to its grille.
Y is the overall width of the product along the rim.
How to determine the permissible ET deviation for a disk
As a rule, each automaker dictates its own permissible deviations for disc offset, and they depend only on the design of the frame, suspension, calipers, wheel arches and other elements of the vehicle. This means that for each car caliper there is a certain indicator of compatibility of various sizes, expressed in the range from minimum to maximum ET in millimeters. So, below are the permissible deviation indicators for the 35 most popular car models in Russia:
Measurable indicators for calculating departure
From this table it can be seen that negative offset is a familiar parameter only for full-size SUVs, and the smaller it is, the more the wheels stick out on them, however, this gives them additional stability on very difficult sections of bad roads; plastic linings around the perimeter of the wheel arches are often as standard. In addition, these brands of cars have a reinforced suspension, a bolt pattern of at least 5x115, which is better than on passenger cars and absorbs bending moment.
What problems can arise due to incorrect selection of disks?
The danger of incorrect selection of this dimension is especially relevant when operating expensive modern cars. Thus, the position of the vehicle on the road is carefully monitored by the on-board computer and various sensors. If a tire goes flat, the driver receives a signal about a loss of pressure; when the brake pedal is pressed sharply, the wheels do not lock, as the ABS is activated.
The same can be said about the directional stability stabilizer, which controls the position of the car on the road and the straightness of its movement, and also prevents skidding on the road, alternately blocking one or another wheel. In this computer, as a rule, engineers enter certain indicators of the wheel rim dimensions - ET, and as the final result - the values of bending moments.
Measuring the jack of the disc
How to correctly measure the offset of an ET disc
What is ET on disks and how to measure it correctly if circumstances are such that there is simply no other way to determine this indicator? Quite often, worn or damaged wheel rims make it impossible to correctly read the markings on their surface, and in this case, vehicle owners have to resort to their measurements.
To select the right wheel rim to replace a product that has expired, you need to determine the ET value on the old wheel by following these steps:
- If the disk is installed on a car, it must be removed using a wheel wrench or a special spanner tool for removing the wheel locks, if any were used when mounting the wheel on the hub. Before dismantling, it is necessary to raise the car with a jack so that the wheel can rotate freely in a hanging position.
- It is necessary to measure the back indentation on the disk, and to do this you must first carefully place the disk on a flat surface with the outer side down.
- The side of the disk that is attached to the hub is on top, and you need to put a wooden measuring rod on it, the length corresponding to the diameter of the wheel. Accordingly, the entire tool must be located on the steel sides of the wheel, and not on the rubber, otherwise the offset will be determined incorrectly, which will lead to errors when purchasing a wheel.
- Using a tape measure or ruler, measure the distance from the mating plane of the disk to the edge of the wooden product. The result is recorded in millimeters.
- The procedure must be repeated, turning the disk upside down, and as a result, the car owner will have 2 indicators recorded - front and rear overhang, which add up to the overall ET indicator through simple calculations.
With the described measurement, the formula ET = (A + B)/2 – B is available to the car enthusiast, where A is the first measurement - the amount of indentation from the rear side, B is the same indicator, but from the front.
Measuring the jack of the disc
Zero offset wheels
Thus, to measure the offset, regardless of whether it is possible to read the markings on the disk or not, the car enthusiast can use the simplest techniques and get a fairly accurate result.
A specific example: the first measurement showed the value A = 143 mm, B = 43 mm. Total value ET = (A + B) / 2 – B = (143 + 43) / 2 – 43 = 186 / 2 – 43 = 93 – 43 = 50 mm. Accordingly, based on this indicator, the vehicle owner must choose the wheels he is interested in in the store.
Of course, in such tables the ET indicator will be present without fail, and, as a rule, engineers do not recommend going beyond the proposed size ranges and absolutely disclaim any warranty obligations in the event of a breakdown of the suspension or other parts.
What is disk offset ET and what does it affect?
Overhang is an important geometric parameter of a disk. The disc simply cannot be put on the hub if it does not fit in size. The discrepancies, as a rule, turn out to be small - the installation of the wheel can still be carried out. But are such experiments permissible? To what extent can the disc offset not correspond to the recommended one? In what direction is the deviation permissible, if it is permissible at all? We will talk about this in the article.
ET disc ejection: what does it mean?
Overhang is the distance from the middle of the disk to the plane of its alignment with the hub. Denoted by the abbreviation ET. The smaller it is, the more the rim will protrude from the outside of the car. The more significant the ET, the more the disk will be recessed. The crash is not affected in any way by the disk parameters. To calculate the load on the suspension mechanism, you only need to know the distance from the middle of the wheel to the hub.
ET must meet the car manufacturer's recommendations. Deviations are unacceptable - even minor ones will cause additional loads on the suspension units. This can cause a reduction in the life of the suspension, and in some cases even leads to its destruction.
You can hear the opposite from sellers. There are many variations of offsets, and therefore store employees don’t really want to select wheels specifically for your car - especially if everything is in order with the other parameters.
Here are some tips for drivers on choosing wheels:
- The appearance of the product should be in the background - technical characteristics are more important.
- You shouldn’t trust sellers too much - you can’t always get reliable information from them.
- Pay attention to the labeling.
What does disc ejection affect?
The offset of the ET affects the wheelbase of the vehicle. If the parameter is changed, the wheel will begin to go outside the body - or, conversely, go inside. All manufacturers clearly regulate it and do not advise allowing even the most minor deviations in any direction. Problems can appear even with a deviation of 5 mm.
Cars vary in handling and stability characteristics. Therefore, each car has its own ET value. Otherwise, the following would happen: with a negative value, the wheel touches the body, and with a positive value, some suspension elements. Only at the values specified by the manufacturer will the level of pressure on the suspension be acceptable.
Here's what happens when there are deviations:
- the steering axis moves;
- bearings wear out prematurely;
- controllability deteriorates;
- tires wear out faster;
- The service life of the suspension is reduced.
What is the flight like?
The parameter can be positive, zero or negative. With positive offset, the center axis of the wheel is located behind the connection to the hub. At zero, the axis coincides with the mating plane. A negative value indicates that the axis is in front of the contact surface.
Nowadays most cars have positive offset. Other options, of course, also occur, but rather as an exception. Negative and zero ET can be found on racing cars, both on track and in full off-road conditions. Their pendants are very different from standard ones.
How is ET disc offset measured?
The parameter is measured only in millimeters. You will need a ruler and a wooden (or metal) strip, the length of which coincides with the radius of the wheel.
- First of all, you need to remove the wheel from the car and put the car on the handbrake. If the wheels have alloy wheels, the procedure will be greatly simplified, since all the nuts on them are open. Otherwise you will have to remove the cap.
- Now you can remove the disc from the wheel. This must be done with a sharp movement.
- The wheel should be placed on the ground with the side opposite the hub. We place a wooden strip on top of the disc rim.
- Then, using a ruler, measure the distance from the surface in contact with the hub to the bottom of the rack - this will be distance A.
- Next, we turn the other side of the wheel towards the ground, and also place the rack on the rim.
- We measure the distance from the bottom of the rack to the plane beyond which the hub is distance B.
Labeling and formula
Calculations should be made using the formula:
The values obtained during the measurement must be substituted into it.
The ET value is prescribed individually for each machine. All the necessary information on this matter is in the car’s operating instructions. Wheels will not fit the vehicle if the measured value differs from the data in this document. “Non-native” components are not worth buying, even if the seller actively convinces you otherwise.
The markings on the discs must be carefully studied - this is the only way to make sure that they are safe to use. Product markings are standard. In any case, the designation contains the letter I or S. The letter I means that the wheel is “identical” and is installed on production cars. S indicates that the wheel is special, that is, its certification is not tied to a specific brand of car. In some cases, there is no letter designation - instead, the name of the plant where the car was made and its catalog number are applied to the rim.
As an example, consider the rim marker 7.5 j x16 H2 5/112 ET 35 d 66.6:
- The first numbers are the width of the disk. For example, 7.5 means the width is 7.5 inches. To convert to centimeters, you need to multiply by 2.54.
- The letter J means that the wheel has some design features. This information is of no interest to consumers.
- X indicates the indivisibility of the disk.
- The number 16 is the wheel caliber corresponding to the tire caliber.
- H2 reports that there are 2 humps on the rim.
- The number 5 is the number of holes for fasteners, 112 is the diameter at which they are located.
- ET 35 speaks of a plus offset, the size of which is 35 mm.
- d 66.6 - central hole gauge. Ideally it should be identical to the hub caliber. If this is not the case, an additional ring must be used to center the fit. It is also called transitional.
How to determine the offset of a wheel rim?
The value obtained from the formula can be either positive or negative (or zero). The parameter determines the distance between the axles of the rear and front wheels, forming a gap between the wheels mounted on the same axle. Rubber, rim and tire parameters do not affect ET at all.
The load to which the car's suspension is subjected can be calculated from the applied load arm - the distance from the middle of the rim to the hub. For each specific car model there can be only one ET - the value of this parameter should not depend on the size of the rim and the tires installed on it. The offset value is written on the wheel. The marker could be like this: ET35. The number 35 means the distance in millimeters. In this case, the distance has a positive value. The distance will be negative if the ET-35 marker is applied, or zero if ET0 is applied.
Conclusion
When buying a wheel rim, don't limit yourself to a visual inspection. Look at the markings. Remember that driving safety depends on the right choice. Use only those items recommended by the manufacturer. And write it down somewhere in the most visible place: departure deviations are unacceptable!
What is a car wheel offset?
As it may seem at first glance, car wheels are a simple solution in terms of design and differ only in design, size and manufacturing materials. However, for different disks, in addition to the basic parameters, there are also additional ones that must be taken into account before purchasing and installing on the machine.
For example, if we consider the parameters of disks, in addition to diameter and width, the marking also contains the designation ET in combination with one or another number. So, et disk means wheel offset. Next, we will look at what disc offset is, what this parameter affects, and how to choose the right discs based on their offset.
Read in this article
What is a disc crash?
- disk diameter;
- disk width (indicated in inches);
- disc offset ET;
- center hole diameter (DIA);
- diameter of the circle of the centers of the holes of the PCD disk (diameter of the location of the mounting holes);
You can also note H or HUMP. This parameter refers to the annular protrusions on the rim that hold the tubeless tire and prevent spontaneous disassembly. In this case, there may be 2 humps on the disk, one, or they may be completely absent. The HUMP itself can be flat, asymmetrical or a combination.
The fact is that it will be difficult to install rims that are not suitable in diameter, width, PCD or DIA on the hub, while a rim with an inappropriate offset relative to the standard one is often installed without any problems (if the deviation is not too large). At the same time, it may seem that such a disk with an abnormal offset normally performs basic functions. Please note that in reality this is far from true.
Even taking into account the fact that stores are actively selling wheels with abnormal offsets and sellers claim that the main thing is to fit the wheel on the hub and also make sure that nothing catches anywhere when driving, this does not mean that the disk can be safely installed on the car.
Moreover, if you also need wheel spacers for rims, then sellers often voice information that reducing the rim offset is quite acceptable and this is not a problem. Let us note right away that in reality this is not at all the case, and the seller’s task is to sell a more or less suitable option that can be installed on the car, and a number of disk parameters are simply ignored and deliberately not taken into account.
If we talk about consumers, naturally, we want to choose the best option not only in terms of design and price, but also in terms of a number of basic parameters, including reach. Let's figure it out.
- To understand what disc offset is, it should be noted that this is the distance between the vertical plane of symmetry of the wheel and the plane of pressing the disc to the hub. The offset is indicated in millimeters.
To calculate the ET departure, the formula is used: ab/2. In this case, "a" represents the distance between the inner plane of the disc and the plane of application of the disc to the hub, while "b" is the overall width of the disc.
Let's move on. Without going into details, you can often encounter disk failure:
As a rule, the first option is the most common. Let’s also add that the offset of the wheels has a direct impact on the width of the wheelbase, since the offset will determine the distance between the centers of symmetry of the wheels on the same axle, taking into account the width.
It turns out that the calculated disc offset (standard) does not depend on the tire size, disc diameter, etc. In other words, the automaker always indicates only one calculated ET parameter for a specific model. On standard disks you can find various ET numbers. As an example, ET 45 indicates positive disc offset, ET 0 indicates zero disc offset, and ET -10 indicates negative disc offset.
Is it possible to install wheels with abnormal offset?
So, owners often install wheels they like on their car with an offset that differs from the standard one. So, this is a gross mistake.
It is important to consider that the disc offset must correspond exactly to that specified by the automaker for a specific car model. In this case, even minor deviations, either upward or downward, are not allowed.
If you install disks with an offset that differs from the calculated factory offset by even 3-5 mm, the operating conditions of the suspension components and parts change, additional forces appear, the vectors of application of such forces change, etc. The result is that the suspension experiences loads that it was simply not designed for.
At the same time, wheel sellers simply neglect to ensure that the wheel offset fully corresponds to the standard parameter for the car. The reason is quite obvious - the range of disk models available for sale is noticeably expanding. Moreover, mistakes are made not only on purpose, but as a result of the unprofessionalism of sellers and the ignorance of the buyers themselves.
More precisely, for one car model, the disc offset may differ. This happens because the car can have different configurations. For example, there is a version with a 2.0 atmo engine and exactly the same with a powerful 3.0 diesel engine. At the same time, during calculations, designers take into account a huge number of parameters, which puts forward strict requirements for chassis parts.
It turns out that for one model with different engines, suspension parts (tie rod ball ends, levers, etc.) may differ. Different internal combustion engines have different weights, which leads to certain elements experiencing different loads when driving.
Taken together, the suspension parts are strictly designed for operation with discs that have a standard offset. Otherwise, the elements that are not the most reliable and durable can very quickly become unusable or collapse right on the go.
As you can see, when the calculated offset of the disk changes, the location of the central axis of the disk relative to the hub changes. If you increase the offset, the wheel will sit deeper on the hub and the wheelbase will narrow. Reducing the disc offset will extend the wheelbase.
Both will mean that the calculated parameters will change. This applies to steering wheel turn, car handling, tire wear, etc. The moments of forces acting on the suspension and the vectors of application of such forces also change. It turns out that the suspension works in abnormal mode, which reduces the service life of the chassis and also affects safety.
In normal mode, if the disks have abnormal overhang, you may not notice the difference, but under conditions of maximum loads and high speeds, the risks increase significantly.
Let’s also add that the original wheels can be installed on the car without any problems, there is no need to use adapter rings, etc. For non-original stamped (iron) disks, the DIA parameter must strictly correspond to the standard one, since adapter rings are not used for steel disks. In the case of alloy wheels, you can adjust the parameter using an adapter ring.
Let's sum it up
As you can see, many car enthusiasts mistakenly do not take into account such a parameter as disk ET when selecting disks for a car. At the same time, sellers often do not strive to select the offset of the car’s wheels (and rims) in full accordance with the factory parameters.
Disc ejection (ET) - what is it and what does it affect?
This article will consider such a parameter as disc offset (ET). What this parameter affects and how much you can change it, what the consequences will be, this will be discussed further. Here the opinion of experts will be formulated, and users will draw conclusions whether they want to conduct these “experiments” or not. So what is ET?
ET is the offset of the disc in relation to the hub. Many car owners get confused all the time, as there is a designation for positive and negative ET. We need to focus on this moment. If you draw a strip along the center of the disk and it corresponds to the line of the disk seats, then this will mean ET-0. When we move the disk seat away from the center of the disk by a few millimeters in one direction or another, this means positive or negative ET. Is it possible to change these parameters, which will differ from the factory ones? Yes, you can. In some cases it is even mandatory. In order to make it clear, you need to try to imagine and understand the operation of a car suspension and the distribution of load on its components.
A little theory
There is a hub. It is mounted on a bearing (bearing inside the hub). A disk with a tire is attached to the hub, and the whole thing rests on the rack. A strut with a spring, in the strut itself there is a shock absorber and in the upper part of the strut there is a fastener that attaches it directly to the car body. That's right - when you are driving and encounter uneven roads or obstacles, the entire force of the impact passes directly to the support point of the rack. How is this checked? The fulcrum, the middle of the bearing and the outer part of the wheel should be in line. If, say, a car owner bought a car and the car clearly follows the line: the support point of the strut - the middle of the hub bearing - the outer part of the wheel, then in this case the car goes smoothly, the suspension “accepts” potholes and uneven road surfaces well. This can be considered the reference state of the suspension. I can't think of anything better here.
Important points
When purchasing rims, many car owners do not want the rims to “sit” inside. Often the user will always reduce the overhang in millimeters, but in practice the disc will come out. Undoubtedly it is more beautiful and everyone wants it. But what this entails is worth finding out.
The edge of the wheel will extend beyond the line (the fulcrum, the middle of the bearing and the outer part of the wheel) according to which, according to the rules, the load should be distributed and if it hits an uneven surface, the steering column will partially take the impact. It will no longer be possible to correctly transfer energy to the support of the rack, since the location of receiving this blow has been changed because the disk has shifted outward. Yes, this impact energy will be partially transferred to the tie rod, which will affect the steering wheel. If there is no hydraulic booster, this will be significantly noticeable, and if there is a hydraulic booster, it will be felt less, but as soon as the car owner changes the disc offset and the wheelbase expands, the driver will immediately feel it. Bumps and shocks will be felt on the steering wheel that were not present with a standard disc offset. Does this give stability? It seems that it does, but at the same time the driver receives a lot of uncomfortable sensations. Few people will like it when some difficulties and shocks occur on the steering wheel.
If you increase ET, that is, we move the disk inward, this often entails such a negative effect - when you turn, your steering wheel will initially spin normally, and then it will begin to pull itself inward, as it were. This feeling is not very pleasant because many car owners are accustomed to turning the steering wheel, then dropping it and it must return to its original position on its own. When changing the disc offset (ET), the driver gets the opposite effect - the driver wants to turn the steering wheel slightly and throw it so that it returns to its original position, but when changing the disc offset, the steering wheel turns and this confuses the car owner and is actually very uncomfortable.
The right approach
If, within reasonable limits, you change the offset by about 10 millimeters, the car owner will hardly notice it. But if the offset is changed to a greater distance, then this will be significantly noticeable. For example, on cars such as an SUV, if the car owner wants to change the offset (ET) without changing the wheels, he can use spacers. This is a completely acceptable method and is widely used among people. Many drivers only change the offset on the rear wheels. From the rear the view becomes much more beautiful. Ahead, this effect is not so clearly visible, but if you install spacers and change the offset, you only get an unpleasant feeling on the steering wheel and a decrease in ride comfort. In general, the car looks at the rear wheels, but not at all at the front. It is extremely rare to find cars in which the front wheels can be seen to be “recessed”. It's not beautiful. This is observed, say, in Lanos and in some other cars of this class. But for the most part, everyone’s front discs look more or less normal. When buying discs, the preference of choice can be given to such a well-known online store as koleso-oz.ru. Here you will find:
- a wide range of
- high quality goods
- caring attitude towards the buyer
If you don’t want to change wheels, but want to change the offset and make a beautiful car, then experts recommend that you try installing not just spacers, but spacers of the required thickness. In a passenger car this thickness will be about 10 mm. The car owner will have to change the bolts if there are studs - it’s a little more difficult, but it’s also possible. Once again it is worth emphasizing that it is advisable to install spacers only backwards. Many people will like this solution. And the fact that the car will not go on track, no one will see it and it will be almost unnoticeable. And this is the proposal of most auto experts - rear spacers. You can always put them on all four wheels, but it’s better to start with the two rear ones. Or, to find out the behavior of your car with a modified stem, first buy and install two spacers on the front wheels and try to drive. If you experience discomfort while driving, feel free to install spacers only on the rear discs. Don't neglect safety. Driving safety is much more important than appearance. If it is comfortable to drive the car with spacers on the front end, then, if desired, you can increase the offset (ET) of all four wheels. But of course, only the rear ones are better. The appearance of the car will change significantly for the better. This is one of the ideal solutions to the issue with departure (ET).
Different "departure"
There is another question: “Why can’t you install disks in front with one offset and in the rear with another?” This is generally not strictly prohibited, but only if it is done correctly. The rear wheelbase of the car should either be the same as the front, or wider, but in no case narrower. This is an important point to remember well. This is the golden rule. As soon as the front wheels are wider than the rear wheels, the car will have a skidding effect when turning - the rear will “run around” all the time. If the car owner increases the wheelbase of the rear wheels, then, on the contrary, the car acquires increased stability in corners.
Conclusion
If you decide to change the ET yourself and move the disks outward, then please approach this issue very carefully. Once again it is worth emphasizing the most important points - if ET is 10 mm, then in principle this is permissible. Well, if you move the disks outward by more than 10 mm, then you need to consult a specialist, because the wheels may begin to “overwrite” with such a non-standard offset.
The situation is simpler on SUVs. There you can even change ET by 30 mm. These will be only the best visually, and nothing will be erased there.