How to find out rim width
Tire and wheel sizes part 1. Marking and selection of car rims.
Marking and selection of car rims. A striking example of how easily different measurement systems can coexist and how deeply this confusion has entered our lives.
- Number and bore diameter of the location of the wheel rim mounting holes. - fastening to the car
- Disc central hole, hub diameter. — fastening to the car
- Wheel rim width. — fastening to the tire (tire)
- Wheel rim diameter. — fastening to the tire (tire)
- Wheel offset. Wheel removal. - wheelbase width
- Disc rim flanges, side flanges. — fastening to the tire (tire)
- Rim shelves and bumpers. - fastening to the tire (tire)
- Other possible designations.
- Wheel mount. The procedure for tightening bolts (nuts).
- Recommended tightening torque depending on the wheel thread diameter
You can familiarize yourself with the decoding of tire designations here.
The number and mounting diameter of the location of the wheel rim mounting holes.
6.5J×15 H2 5/112 ET39 d57.1 - “five holes with a diameter of 112 mm”
The second number is the diameter in mm at which the centers of these holes are located, which is called PCD = Pitch Circle Diameter and in our case it is 112 mm. In the tire industry, for chic, both of these parameters are often called “PCD”, and when indicating the PCD of a disk they write 5/112. The wheel mounting holes are located at different diameters with tight positional tolerance in relation to the central hole. There is a limited number of such diameters (examples are 98, 100, 112, 114.3, 120, 130, 139.7 and some others; they are used by automakers either by tradition or as the most suitable for certain types of cars - for example, size 139, 7 is typical for pickups and SUVs). Occasionally there are wheels with two “sets” of 4 or 5 mounting holes, located on two different diameters.
Disc central hole, hub diameter.
6.5J×15 H2 5/112 ET39 d57.1 - “hole for hub 57.1 mm”
d 57.1 - Diameter of the centering hole on the disk. Must exactly match the diameter of the landing cylinder on the hub. Often the same wheel (wheel rim) is offered for cars from different companies, so the central hole in the wheel rim must be different. Because in addition to the centering function, the landing cylinder has another, no less important one - it partially takes on the load that falls on the mounting bolts (studs). Therefore, if the centering hole of the disk you like is larger than the hub mounting cylinder, you will have to use special centering rings, which can be bought at tire centers, or ordered somewhere. The external and internal dimensions of the centering ring must correspond exactly to the diameters of the hub cylinder and the centering hole of the disk, respectively.
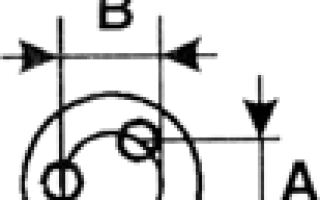
Wheel rim width.
A disc wheel consists of two main parts: the rim and the disc itself. The disc is the central part of the wheel, with which the wheel is attached to the car hub with bolts or nuts. The rim is a cylindrical part of a wheel with a special profile, which is located perpendicular to the disk and serves to mount a rubber tire on it.
6.5 J×15 H2 5/112 ET39 d57.1 - “disc (rim) seat width 6.5 inches”
DIMENSIONS: always given in inches (1 inch = 25.4 mm), except for Michelin designs, which give dimensions in millimeters.
ATTENTION: The width and diameter are selected according to the size of the rubber tire. To determine the overall width of the wheel rim, add another 26 mm to the rim width value on the marking. that is, the thickness of the outer and inner side edges. The overall width of the rim should be 12 (plus or minus 4) mm less than the width of the rubber tire profile
Wheel rim diameter.
6.5J× 15 H2 5/112 ET39 d57.1 - “wheel diameter (size) 15 inches”
15 – landing (!not overall!) diameter of the wheel rim in inches, which must correspond to the landing diameter of the tire. Passenger cars use wheels with a diameter of 12 to 32 inches, the most common diameters being 14-16 inches. 1 inch=25.4 mm.
Wheel offset . Wheel removal.
Disk offset is the distance between the mounting plane of the wheel (the plane of which the disk is pressed against the hub) and the middle of the disk width (an imaginary plane passing through the middle of the rim).
To determine the wheel offset, you need to measure dimension “B” on the inside of the wheel. Divide size “X” in half. Subtract size X/2 from size “B”. If the difference is positive, then the offset is positive; if it is negative, then the offset is “negative”. Or, in other words:
The offset is “positive” if the mating plane does not go beyond the imaginary plane.
The offset is “negative” if the mating plane passes through an imaginary plane.
Disc rim flanges, side flanges.
6.5 J ×15 H2 5/112 ET39 d57.1 - “type J rim flange”
J (JJ, JK, K,B, P, D...) This letter encrypts technical information about the edges of the disc rim (design, shape, height). The most common types of disks today are J (mainly for single-wheel drive vehicles), and JJ (usually for all-wheel drive). The flanges of the rim of the rim affect the installation of rubber, compensating weights, as well as the resistance to displacement of the tire on the rim in extreme conditions. Obviously, despite the external interchangeability of, for example, J and JJ disks, it is still better to choose the parameter recommended by the car manufacturer.
Wheel rim and champa shelves.
6.5J×15 H2 5/112 ET39 d57.1 - “shelves rims and humps type H2”
H (H2, FH, AH, CH...) – these letters encrypt information about the design features of the disk rim flanges and the protrusions (hamps) on them. Humps are designed for tubeless tires and ensure correct installation of the tire on the rim. Some tires require special wheel parameters in this regard; this point needs to be clarified when purchasing tires. In general, a car enthusiast does not need to delve deeply into the essence of these designations.
Other possible designations.
The disk may also indicate:
- Date of manufacture . Usually a year and a week. For example: 0504 means the disc was released in week 5 of 2004.
- SAE, ISO, TUV, PCT. - stamp of the regulatory authority. The marking indicates that the wheels comply with international rules or standards.
- MAX LOAD 2000lb - a very common designation for the maximum load on a wheel (denoted in units of mass - kilograms or pounds). The maximum load listed here is 2000 lbs (908 kg).
- MAX PSI 50 COLD - means that the tire pressure should not exceed 50 psi (3.5 kgf / sq. cm), the word COLD (cold) means that the pressure should be measured when the tire is cold.
- Other
About the width of the car rim
Reading time: 6 minutes
Many drivers and vehicle owners who have been using them for at least 4-5 years have been faced with the problem of choosing new rims. Thus, most of them, not having a professional relationship with the automotive industry, firmly know only one value - radius, which is often incorrectly confused with the radius of the disk. However, in addition to these rim diameter indicators, the disk also has a width characteristic, which greatly influences the further choice of tires and the fit of the product under the wheel arch of a particular car.
Disc rim width: what is it?
The width of the rim of a wheel is its geometric characteristic at which the greatest distance from edge to edge of the beads intended for mounting the tire is greatest. This value, in accordance with international standards, has the following features:
Basic parameters of the wheel rim
- First of all, it is expressed in inches, and if the car enthusiast himself measures this value using a tape measure, then the reading of the distance from the edge to the edge of the wheel in millimeters should simply be divided by 25.4 mm and get the same dimension, but in inches.
- The limits of this value for passenger cars range from 3.5 to 13 inches, which corresponds to the actual width of the product from 87.5 to 279.4 mm. The division step of this characteristic is 0.5 inches, that is, the product can be 5, 5.5 or 7.5 inches, but never 4.4, which is quite easy to round to the nearest value when measuring the parameter with your own hands.
- For each disc radius, the width indicator varies and has acceptable ranges, such as for R15 - from 3.5 to 7.5 inches, and for R18 - from 7.5 to 13 inches. Thus, online or in the system of sellers at a specialized retail outlet, you can find the corresponding table of acceptable ratios of these indicators depending on the diameter of the disk and its offset.
What is the width of the wheel rim measured in and what does it affect?
How to correctly measure the width of a wheel rim
To accurately determine the rim width in inches on any wheel, regardless of its manufacturing method and other parameters, the driver must do the following:
- For an accurate measurement, you should remove the wheel and bleed the air from it.
- Next, the tire is removed from the rim and set aside, since it is not involved in the measurements.
- A car enthusiast takes any tool for measuring with a fairly high degree of accuracy - a tape measure, ruler or caliper. The main thing is that the device can completely cover the entire width of the wheel with a margin.
- The distance from edge to edge of the rim is measured, strictly perpendicular to the radius of the product.
- The result is analyzed and reduced to the nearest value in inches. For example, if a size of 189 mm was obtained, then after dividing it by 25.4 the result is 7.44 inches. As stated above. The division step of the inch scale for wheels is 0.5, that is, the closest parameter to the measurements obtained is 7.5 inches, and it is this parameter that must be purchased.
- At the end of the process, the wheel is mounted back, inflated or replaced immediately after purchasing a new product to replace the damaged or worn one.
- If the driver is unable or does not want to engage in such a long procedure, then, provided that the original wheels and tires are selected in accordance with the table according to all the rules, he can use a simple ratio of values.
Disc offset diagram
This means that each rim is approximately 25% narrower than the tire, and by measuring the width of the rubber sole he can always adjust the measurements to the required results. So, for example, if the tire width is 285 mm, then 75% of this size is 213.75 mm. Dividing this figure by 25.4 mm, the result is 8.41 inches, which corresponds to the standard disk size of 8.5 inches.
What does the rim width of an alloy wheel affect?
The width of the rim is an extremely important indicator when choosing wheels for a specific make and model of car, since other indicators also depend on it. Thus, the main characteristics of the technical equipment of the vehicle, which are affected by the width of the disk, are listed below:
- Wheel offset or ET indicator, calculated in millimeters, which can be either negative - from -25 mm to 0, or positive - from 0 to 50 mm for almost all brands of passenger cars. This parameter, as a rule, should vary depending on the width of the disk, and the smaller it is, the more the disk moves away from the hub, to the point that it can protrude beyond the side dimensions of the body.
Otherwise, he risks choosing a tire with a too low profile, which will cost more than the standard option, and when driving the car will behave very roughly, causing discomfort to the driver and passengers in the cabin.
- Car enthusiasts should remember that too wide rims behave better on off-road and loose snow and can affect keeping the car in its track without skidding, which is convenient for SUVs or for any vehicles in winter. This is achieved, first of all, due to the fact that the pressure from the wheel per unit area is significantly reduced as the support area increases.
- At the same time, for summer driving, too wide wheels are not needed, because they will cause additional friction on the asphalt, which will reduce the dynamic characteristics of the car and significantly increase fuel consumption.
Disc with width 12J
Rim protection
It happens that drivers choose tires that do not exceed the width of the rim by 25%, as stated in the standard requirements and recommendations. So, a tire that is too narrow, of course, will fit on the wheel, but it will cease to be a kind of bumper for the cast product. In addition, a car enthusiast can choose to use wheels with zero or negative offset, which will also be risky for the safety of the disk, especially when parallel parking near a high curb.
This product performs the following functions for the wheel and the car as a whole:
- As mentioned above, this is protection from external mechanical influences when driving, parking or in the event of an accident.
- As a rule, these products are made in bright red, green, yellow or other colors, and this significantly attracts the eyes of others, highlighting the car with a unique sporty style.
- Any driver can purchase a disc without this device, and purchase it separately, knowing only the radius of his wheel.
- With such protection, the owner of the vehicle can install wheels of any width, if the characteristics of the car itself allow it, and not worry about their damage.
To be confident in choosing the wheel width, the driver only needs to study the configuration of his car and purchase a product whose geometric parameters do not differ from those that are installed in the basic version on the car when it comes off the assembly line at the factory. Thus, before launching the next modification into mass production, engineers of any automaker carefully calculate all the indicators and parameters of each part, as well as their impact on the design of the vehicle.
Dimensions and parameters of car wheels
The selection of car wheels should be treated with great care and attention! Each disk has several parameters for installation on a car, each of which must be taken into account when choosing. Some parameters are unchanged, while others can be adjusted within a small range. This article will tell you about all the intricacies of choosing cast and forged wheels.
Disk options
Size A (rim diameter in inches) – seat diameter – the diameter of the annular part of the rim on which the tire rests.
Dimension B (rim width in inches) - rim seat width - the distance between the inner surfaces of the wheel flanges. Determines the possible profile width of the installed tire. A deviation of 0.5-1 inch in the seat width is allowed, but for low-profile tires it should be minimal.
HUMP ( width in inches) – an annular protrusion, used for additional fixation when installing tubeless tire beads.
ET (offset in mm) – offset (offset) of the disk, i.e. a parameter that determines how deep the wheel is recessed into the car arch. The offset is the distance from the plane of the disk adjacent to the car hub to the plane passing through the axial middle of the width of the disk rim. For each vehicle, the manufacturer provides a list of acceptable wheel installation options. This parameter can be changed by +/- 5 mm without harm to the car's suspension. If the deviation is large, it is necessary to try on the disc on both the front and rear axles of the car, since it is possible that the disc will rest against suspension elements, fender liners or parts of the car’s brake system. In addition, installing wheels with an offset that is significantly less than intended leads to a significant decrease in vehicle stability in corners, increased steering sensitivity to road irregularities and uneven braking forces.
PCD – the number of mounting holes and the diameter of the circle of the centers of these holes. This value must correspond to the standard value, otherwise it is impossible to achieve reliable fixation of the wheel on the car hub. A deviation of even 1-2 mm can lead to misalignment of the wheel and fastening elements.
DIA (CO in mm) – diameter of the central hole of the disk. It must match the diameter of the centering protrusion on the vehicle hub. An upward deviation of its value is allowed. In this case, adapter centering rings are used to install the wheel.
Disk parameters can be indicated as follows, for example:
6×15 ET45 5×100 D57.1
6 – rim width in inches;
15 – disc diameter in inches
ET45 – disc offset (in mm);
5×100 – PCD , the number of mounting holes at a certain diameter location. It must be taken into account that for each car it (diameter) is different and cannot be changed under any circumstances;
D57.1 – DIA (TsO) diameter of the central hole of the disk, measured in mm;
6.5 J 15 H2 5×114.3 ET45 D54.1
6.5 – rim width in inches;
15 – disk diameter in inches;
5×114.3 – PCD , number of mounting holes at a certain diameter location.;
ET45 — disc offset (removal) (in mm);
D54.1 – DIA (TsO) diameter of the central hole of the disk, measured in mm;
J and H2 are symbols needed more by specialists. J encrypts information about the design of the rim flanges (can be JJ, JK, K or L) . And H2 is the design code for humps, ring protrusions on the rim flanges that serve to reliably hold the tubeless tire on the rim (there are many variations: H, FH, AH, etc.);
Wheel and tire size matching table
Sooner or later, every motorist will face the question of buying new wheels and tires. Some drivers prefer to install alternative wheels for their car, others choose standard sizes. To choose the right tires for wheels and vice versa, you need to know the parameters of these components for your car.
Installing wheels and tires with incorrect parameters will negatively affect handling and will also accelerate wear of the chassis. The table of tires and wheels will help you understand the issue and buy the necessary components. The table shows tire sizes and wheel characteristics.
Features of selection of wheels and tires
A tire is placed on the rim of the disk; accordingly, the width of the tire profile must match the profile of the disk. In recent years, there has been a fashion for installing larger rims; car manufacturers do not recommend taking this step. If there is a large difference between tires and disks, the contact patch will be uneven, resulting in a loss of controllability.
The proportionality of tires and wheels is worth studying from two sides:
- The selection of tires and wheels is carried out according to the recommendations of your car manufacturer. You open the instruction manual and look at the dimensions, for example, you need to install R13 wheels, based on this indicator you select the recommended tire size.
- The second side is fitment (checking the position of the wheels relative to the arches, studying the fit of the tires). Fitting is carried out in cases where there is a low landing, negative camber or other tuning features.
Wheel and tire markings
A motorist who is going to buy wheels should know their markings and tire size. Let's look at it using the example of the R13 4x98 D58.6 ET35 J5 disk:
- R13 – wheel rim diameter, indicated in inches;
- 4x98 – the number “4” indicates the number of holes for fasteners, as for the number “98”, it indicates the diameter of these holes in millimeters;
- D58.6 – the disc is installed on the hub, and D58.6 indicates the diameter of this hole in mm;
- ET35 denotes the distance from the center of the disk to the mating surface, in other words, the offset, indicated in mm;
- J5 – rim width in inches.
We've looked at the wheel sizes, now it's worth finding out how to calculate the tire size. For example, let's take tires with size 135/80R 13:
- The letter “R” denotes the design of the tire, in our case it is a radial tire;
- The number “135” indicates the profile width in millimeters;
- The number “13” is the diameter of the inner circumference of the tire, which is indicated in inches;
- The number “80” indicates the ratio of height to width, in this case it is 80%.
Choosing the right wheels and tires
If you want to maintain the safety indicator, you should not change the diameter of the circle of the centers of the mounting holes, that is, PCD disks. That is, the tire and wheel sizes must comply with the recommendations. Installing tires and wheels with a slight discrepancy is allowed, but in this case you need to use fastening bolts with eccentrics.
Thanks to these elements, it becomes possible to install rims with 100 mm PCD on machines where rims with 98 mm PCD should be installed. Also, the sizes of car tires and wheels must match the central holes. In some cases, this requirement cannot be met; an adjusting ring will help solve the problem.
Helpful advice! The mounting ring has the same outer diameter as the disc. As for the internal diameter, it corresponds to the diameter of the hub. If this component is installed correctly, you will maintain your vehicle's performance.
Wheel to Tire Ratio Table
Study the table and find your option. The table of tires and wheels by size allows drivers who have not previously encountered the issue of replacing wheels and tires to find the required sizes:
Download the tire and wheel correspondence table in .doc format: Tire and wheel correspondence table
Disc markings, symbols, terms on discs, designations
To choose wheels for your car, it is not enough to know the required diameter and the number of bolts for fastening. The disk must meet a number of parameters. The full disk size looks like this: 6.5×16 5/100 ET48 d56.1 . The ability to decipher symbols on disks will help you avoid mistakes when purchasing and disappointments when installing them on a car.
6.5 - rim width value . Indicated in inches. If you want to know the size in millimeters, then 6.5 must be multiplied by 2.54 (1 inch).
j (can be replaced by “ H2 ”) - for ordinary consumers these values are not important, because are service designations for manufacturers and sellers.
J is a value that encodes data on the design features of the edges of the rim flanges, such as their angles of inclination, radius/radii of curvature, etc.
H2 (short for Hump) - the presence of this designation indicates that there are annular projections (humps) on the rim flanges that keep the tubeless tire from sliding off the rim. The letter designation H means single (simple) hump. H2 - stands for double hump. There is also a Flat Hump - FH , Combi Hump - CH , Asymmetric Hump - AH . If there is an x sign between the designations of the width of the disk and its mounting diameter (as in this case), this means that the disk rim is one-piece, without humps.
5/100 - indicates the PCD value of the wheel (Pitch Circle Diameter). The number “5” is the number of fastening holes for nuts (bolts) on the disk, and in millimeters “100” is the diameter along which the fastening holes are located. If necessary, and there are no special instruments at hand, measurements can be taken with a regular stationery ruler.
IMPORTANT: The wheel mounting holes can be located on different diameters, which have a very tight tolerance relative to the central hole.
Warning! The mounting holes may have a small plus tolerance in diameter, which visually makes it difficult to accurately determine the PCD if it differs from the standard one by only 2 millimeters. For example, a wheel with a PCD value of 4/98 is often installed on a hub with a PCD value of 4/100. IS IT DANGEROUS. Only one nut (bolt) will be fully tightened. The mounting holes of the remaining 3 nuts will “lead”, as a result they will be undertightened or tightened skewed. As a result, the wheel will not be completely seated on the hub. When driving it will “beat”, there is a high risk that the nuts will gradually unscrew by themselves.
d - (example: d 66.6) - in millimeters indicates the diameter of the hub , or the value of the diameter of the central hole of the wheel. It is important that this parameter exactly matches the diameter of the vehicle hub mounting cylinder. Matching the sizes will ensure preliminary centering on the wheel hub, which will facilitate installation of the bolts.
ET - letter designation of disc offset , i.e. distance in millimeters from the mating plane of the wheel rim mounted on the car hub, and a conditional plane that runs in the middle of the wheel rim.
ET “positive” - the mating plane does not protrude beyond the conventional boundary.
ET “negative” - the mating plane is behind the imaginary plane.
In some countries, there is another designation for ET - OFFSET or DEPORT.
Examples of departure designations:
ET 46 - positive offset, 46 millimeters.
ET-20 - negative offset, 20 millimeters.
ET 0—zero offset.
Warning! It is dangerous to install wheels on a car whose disc offset differs from the standard one recommended by the car manufacturer. In an effort to give the car a sporty look, some car owners install wheels with a reduced offset. The car becomes a little more stable on the track, because... the wheel track becomes wider. And at the same time, the load on the car’s suspension and wheel bearings increases. And vice versa, it is impossible to increase the wheel offset - its wheel rim will rest against the brake disc. All this can lead not only to car breakdown, but also to an emergency on the road.
The wheel may also have the following symbols:
— Date of manufacture — (example: 0309) — means that the release date of the disc is the third week of 2009.
- ISO, SAE, TUV - the mark that is given by the regulatory body. This marking is confirmation that the wheel complies with international standards/rules.
— MAX LOAD 2000LB is the most commonly used value for the maximum wheel load capacity (in pounds or kilograms). In this example, the maximum permissible load limit is 2000 pounds, i.e. 908 kilograms. — PCD 4/100 — parameters of connecting dimensions; — MAX PSI50 COLD — maximum air pressure in the tire. In this example, no more than 50 pounds per square inch (3.5 kgf/sq.cm). “COLD” - translated as “cold” - a reminder that pressure measurements must be taken in a cold tire.
Recommendation from specialists at the online wheel store Kolesa Darom
Even if you feel that the technical terms are more or less clear to you, it is still better to select disks by consulting with a specialist directly at the time of purchase. This, at a minimum, saves money and time. And, as a maximum, it will save you from mistakes and, as a result, dangerous situations on the road.