Road accident consequences and types of liability
What liability can there be for an accident?
The type and degree of liability in an accident depends on the consequences of the offense committed. Russian legislation establishes 3 types of liability for causing harm or damage to another person:
- civil liability, which consists of the obligation to compensate for material and moral damage caused to the injured party;
- administrative responsibility, which consists in the execution or serving of a sentence imposed by a court or an authorized body for committing offenses provided for by the Administrative Code;
- criminal liability, which consists of serving a sentence imposed by a court for committing an offense under the Criminal Code.
Civil liability in case of an accident
According to the provisions of Article 1079 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, a citizen who causes damage to another person as a result of an accident is obliged to compensate him morally and materially. Often, compensation for damage is assigned to several people depending on the degree of their guilt in the incident, for example, the driver who committed the accident and the owner of the vehicle who provided the car to the offender. Thus, the owner of a car whose driver commits an accident inevitably becomes an accomplice to the incident and a co-defendant in restoring the damage, provided that the car was transferred to the driver’s control legally.
The owner is released from liability for compensation for damage to victims only in cases where his car was stolen, the accident was caused by force majeure, or the accident was committed with the intent of the victim. It should be remembered that when transferring control of a car by proxy to another person, civil liability for damage remains with the owner of the vehicle - a source of increased danger to surrounding people.
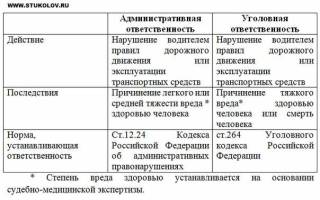
Administrative liability in case of an accident
Violations of traffic rules that pose a threat to traffic safety, health and life of participants give rise to administrative liability, the degree of which is determined depending on the consequences that occur in accordance with the relevant paragraphs of the Code of Administrative Offences. A road accident involves causing material damage, harm to health or death of the victim. The jurisdiction of administrative liability extends from causing varying degrees of material damage to causing light and moderate harm to health.
If a slight degree of harm is caused, administrative liability is limited to a fine of 2,500 to 5,000 rubles or excommunication from driving for 1-1.5 years on the basis of Article 12.24 Part 1 of the Administrative Code. If an average degree of harm is caused, Part 2 of the same article of the Code determines a fine in the amount of 10-25 thousand rubles or a suspension from driving for 1.5-2 years.
The degree of harm caused to health can only be determined by a forensic expert based on the examination performed and the duration of the recovery period as a result of documented treatment. Mild health harm refers to mild concussions, hematomas, bruises, dislocations and other injuries when the victim’s loss of ability to work, confirmed by a sick leave certificate, ranges from 1 to 20 days. Damage to health of moderate severity is recorded with moderate concussions, fractures and other injuries, when the loss of ability to work exceeds 21 days.
Compulsory civil liability insurance for car owners introduced in Russia allows victims to receive material compensation for damage caused, including harm to health, in the amount of up to 500 thousand rubles from insurance companies. If the damage incurred exceeds the established maximum insurance, then the remaining amount must be paid to the victim by the culprit of the accident from his own pocket.
Video: Responsibility for an accident resulting in harm to health #accident #driver's responsibility
Criminal liability in case of an accident
In the event of the death of a victim in an accident or the infliction of serious damage to health, liability is imposed on the culprit in accordance with the provisions of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. Its degree is determined by a court decision, taking into account all mitigating and aggravating circumstances identified and proven during the investigation and trial. The court also establishes the amount and procedure for compensation for loss of ability to work or loss of a breadwinner to the victim.
Severe harm to health in an accident includes injuries that resulted in loss of functionality of individual human organs, termination of pregnancy, irreversible facial disfigurement, mental impairment, complete or partial but permanent loss of ability to work. Article 264 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation establishes the following degrees of criminal liability for causing grievous damage to health in an accident due to negligence:
- arrest for 6 months;
- correctional labor for up to 24 months;
- restriction of freedom for up to 36 months;
- imprisonment up to 24 months.
In addition to the listed penalties, mandatory deprivation of the right to drive a car for up to 36 months is also used.
The death of a victim in an accident also increases the liability of the culprit as follows:
- in case of death of one person - up to 4 years of forced labor or up to 5 years of imprisonment. If this is aggravated by the drunken state of the perpetrator of the incident, then one punishment is provided - imprisonment for up to 7 years;
- when causing the death of several people in a sober state, forced labor increases to 5 years, and imprisonment increases to 7 years. For a drunk driver, the death of several people in an accident faces imprisonment for 9 years or forced labor for up to 7 years.
In these cases, there is also a mandatory deprivation of rights for three years.
During the investigation, the investigating authorities must check all versions, factors and circumstances of the incident that could have influenced or caused the accident. These include:
- presence of a traffic violation and who first violated the rules - the driver, the victim or a third party;
- compliance with vehicle operating rules;
- the condition of the road surface, violations in its maintenance and service in terms of ensuring traffic safety;
- negligence or intent of the victim, including for the purpose of suicide;
- intentionally causing an accident with the intent to kill or intimidate;
- staging an incident to conceal another previously committed crime;
- an accident, an act of nature or other force majeure.
The person accused of committing an accident has the right to:
- use the services of a lawyer at any time;
- know the charges;
- provide explanations on them, evidence of your innocence, petitions and complaints about unfounded and illegal actions of the investigative authorities;
- get acquainted with the materials of the case and the protocols of the investigative procedures carried out with him at the end of the investigation;
- meet and correspond with lawyers and relatives during detention.
Detention of traffic violator
The law provides for two types of detention
- administrative detention. The period of detention is no more than 3 hours; it is used in case of an administrative offense or to establish an identity;
- criminal procedural detention. The period of detention is up to 2 days, applied in case of suspicion of committing a criminal offense. After this period, the detainee either must be released, or he must be charged and then he can be detained until trial.
When a criminal case is initiated, the car may be arrested and, based on the decision, seized as material evidence.
Responsible storage of the car can be entrusted to relatives, organizations or other persons against a receipt guaranteeing safety. Storage of material evidence lasts until the court verdict is pronounced and its term expires. A court decision may confiscate the car as compensation for damage to the victims. The arrest of vehicles is carried out only if there is such a need and is carried out with the execution of a protocol, which indicates the cost of the car, a list of property and equipment. A copy of the protocol is given to the owner of the car.
Fine for an accident to the culprit of the accident in 2019
“I am to blame for the accident. And that, in addition to my compensation for material damage to the injured party, I must also pay a fine for violating traffic rules!?” Drivers often believe that in the event of a traffic accident and they admit their guilt, they will not be brought to other administrative or even criminal liability. And they are mistaken about this.
Classification of types of liability
Russian legislation in terms of traffic violations provides for three types of liability for those responsible for road accidents.
Civil responsibility
According to it, the culprit of the incident is obliged to compensate the injured party for the harm he caused in full (Civil Code of the Russian Federation, Article 1064. “General grounds for liability for causing harm”).
Administrative responsibility
Applies to those responsible for road accidents who also violated traffic rules. According to the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, Chapter 12: “Administrative offenses in the field of road traffic,” four types of liability may be applied to the perpetrators:
1 Fine from 500 to 30,000 rubles.
2 Deprivation of driving privileges: from one month to two years.
3 Arrest for up to 15 days.
4 Mandatory correctional labor for a period of 100 to 200 hours.
These types of liability apply in cases where there are no fatalities in an accident and in the case of no serious harm to health. It should be remembered that the fine to the culprit of the accident for an accident can be paid in half within 20 days from the date of the decision on the fine (Administrative Code of the Russian Federation, Article 32.2, Part 1.3).
Criminal liability
Occurs for the culprit in an accident when serious harm to health is caused to one or more persons or when the death of this person or persons occurs. Alcohol intoxication aggravates the guilt and increases the punishment of the culprit (Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, Article 264. “Violation of traffic rules and operation of vehicles”).
Fine for the culprit in an accident
It is necessary to distinguish between civil liability arising from an accident and administrative liability (fines for the culprit in an accident): in the first case, compensation is provided to the injured party by the culprit and/or his insurance company, and in the second, payment for traffic violations goes to the state budget.
Let's consider specific violations and fines that can be issued to the culprit of an accident, according to Chapter 12 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation:
if the vehicle of the culprit of the accident is not properly registered (there is no vehicle registration certificate), the culprit will be issued a fine in the amount of 500 to 800 rubles; (Article 12.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation);
if the license plates of the culprit’s car are installed incorrectly (not in the right place, upside down), a fine of 500 rubles; if no fine is established at all, a fine of 5,000 rubles or deprivation of the right to drive a motor vehicle; if the license plates of the culprit are obviously false, a fine of 15,000 rubles to 20,000 rubles and deprivation of the right to drive a motor vehicle; (Article 12.2 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation);
if the culprit of the accident was driving a vehicle and did not have registration documents for the car and/or an insurance policy, a fine of 500 rubles; (Article 12.3 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation);
if, after an accident, red lights or red reflectors are found in front of the culprit’s vehicle, a fine of 3,000 rubles; if special sound and light signals (flashing lights, horns with the characteristic sound of special services vehicles), taxi lights (the so-called “checkers”) are installed illegally, there is an illegal sticker of color graphics of operational services or a “disabled person” sticker, a fine of 5,000 rubles is issued; (Article 12.4 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation);
if the culprit of the accident was driving a vehicle with a malfunction or under conditions where it is prohibited to use the vehicle, a fine of 500 rubles; (Article 12.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation);
if the culprit of the accident was not wearing a seat belt or did not have a motorcycle helmet while riding a motorcycle, the fine is 1,000 rubles; (Article 12.6 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation);
if the culprit of the accident did not have a license to drive a vehicle, he will be issued a fine of 5,000 to 15,000 rubles; if the culprit was deprived of his driver’s license, the fine will be 30,000 rubles; (Article 12.7 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation);
if the culprit of the accident was intoxicated (alcohol or drugs), the fine will be 30,000 rubles; (Article 12.8 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation);
if at the time of the accident the culprit was driving through a prohibiting traffic light, a fine of 1000 rubles will be issued; (Article 12.12 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation);
if the culprit of the accident violated the rules for driving through the intersection (did not provide the right of way or drove out during a traffic jam), the fine will be 1,000 rubles; (Article 12.13 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation);
if the culprit of the accident did not give a signal when changing lanes or maneuvering, did not take the appropriate position when turning or turning, made a U-turn or moved in reverse where this was not provided, entails a fine of 500 rubles; (Article 12.14 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation);
if during an accident the culprit was moving along the side of the road or joining an organized convoy, the fine will be 1,500 rubles; (Article 12.15 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation);
if the culprit of the accident was moving on bicycle paths or sidewalks, a fine of 2,000 rubles will be issued; (Article 12.15 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation);
when the culprit of an accident drives into oncoming traffic or onto tram tracks in the opposite direction to avoid an obstacle, the fine will be from 1,000 to 1,500 rubles; and if it was driving in the oncoming lane or tram lines in the opposite direction, the fine will be 5,000 rubles; (Article 12.15 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation);
If during an accident the culprit did not fulfill all obligations, according to the Rules (turning on the hazard warning lights, installing an emergency stop sign), the fine will be 1,000 rubles.
These are the main types of violations and fines that are committed by those responsible for road accidents. A complete list of fines and methods for calculating them are given in Chapter 12 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
In case of any accident with any degree of severity of consequences, we recommend that you contact lawyers or any specialists competent in the legal field.
Fine for an accident - what is the responsibility for the culprit of the accident in 2019
Asking a lawyer is faster than reading!
Ask a question right now and get a free consultation. We will respond within 5 minutes and solve even the most difficult situation.
Road accidents are, unfortunately, a common occurrence. Therefore, every motorist needs to know the laws regarding road accidents, what punishment he faces, what the fine is if he gets into an accident and is at fault. Liability measures for road accidents depend on the severity of the violation that provoked the collision and the severity of the consequences. If people were seriously injured in a disaster (even to the point of death), then the penalties are regulated by the Criminal Code (CC) of the Russian Federation. If there were no fatalities, then liability is considered by the Code of Administrative Offenses (CAO) of the Russian Federation.
Fine for an accident to the culprit of the accident in 2019
The guilty citizen bears the burden of three types of liability in an accident:
- civil. This means that the perpetrator must compensate the victim for the harm caused. This obligation is spelled out in Art. 1064 of the Civil Code (Civil Code) of the Russian Federation: “Harm caused to the person or property of a citizen, as well as harm caused to the property of a legal entity, is subject to compensation in full by the person who caused the harm.” Compensation is carried out either by the insurance company (IC) of the culprit, or by the citizen himself;
- administrative. It is assumed that the culprit must pay for the traffic violation that caused the car accident. Punishment for road accidents is regulated by Chapter 12 of the Code of Administrative Offenses. Depending on the seriousness of the violation committed, the culprit may be charged with:
- Penalties up to 30 thousand rubles;
- Ban on driving a vehicle (vehicle) for up to 2 years;
- Arrest up to 15 days;
- Correctional work up to 200 hours.
- criminal This liability is imposed if people are seriously injured or killed as a result of a car accident. Maximum liability under the Criminal Code is 9 years in prison.
Thus, a fine for an administrative offense (up to 30,000 rubles based on the severity of the offense), paid to the state treasury, does not annul penalties in the context of civil and criminal liability.
Fine for failure to maintain distance in an accident
Failure to maintain a certain interval between vehicles when driving is the most common cause of accidents. The traffic rules (clause 9.10) prescribe: “The driver must maintain such a distance to the vehicle moving in front that would allow him to avoid a collision, as well as the necessary lateral interval to ensure traffic safety.” In this case, the condition must be met: both cars must move. If one of the vehicles is standing, then the provision on maintaining distance loses all meaning. As a rule, when driving forward, the citizen driving the car behind is at fault for the collision. What is the fine for violators for road accidents where the distance is not maintained? According to Art. 12.15 (part 1) of the Code of Administrative Offenses, this penalty is 1,500 rubles.
Fine for creating an emergency on the road
An emergency situation on the road can be triggered by any failure to comply with traffic rules. Let's consider the most common offenses and the traffic police fines applied to them for the owner of the vehicle:
What are the dangers of an accident when driving in reverse? Drivers use reversing for parking, leaving a parking lot, and when making a U-turn. Reversing is prohibited :
- at a crossroads;
- in a tunnel, on a bridge, overpass;
- at a pedestrian crossing;
- on highways and main roads;
- within and in front of railway crossings;
- at public transport stops;
- in areas with poor visibility.
The punishment depends directly on the nature of the violation committed and the consequences. Thus:
- moving on the highway in reverse will cost the driver 2,500 rubles;
- Such a maneuver at a railway crossing will result in deprivation of rights for six months or a fine of 5,000 rubles.
Fine for not having a warning triangle
Every vehicle must have an emergency sign. This is prescribed by the traffic rules in the list of conditions under which the vehicle is prohibited from operating, in clause 7.7. This sign is intended to warn road users about the source of danger on the roadway. After an accident, the vehicles involved in the accident become such. What happens if you don’t put up a warning triangle? The absence of a sign, according to Ch. 12.5 of the Administrative Code (Part 1), punishable by payment of 500 rubles. If the driver has this sign, but was not placed on the road during the accident, then the punishment, according to Art. 12.27 (part 1) Code of Administrative Offenses - 1000 rubles.
Criminal liability
A criminal case under an article of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation is initiated if people were injured in a disaster. In this case, their health was seriously damaged or one or more people died. Liability for such a car accident is regulated by Art. 264 of the Criminal Code and is being investigated by an accident investigator. If, as a result of a road incident, damage to health was caused, then the culprit (Part 1 of Article 264 of the Criminal Code): “... is punishable by restriction of freedom for up to three years or forced labor for up to two years with deprivation of the right to occupy certain positions or engage in certain activities for a term of up to three years or without it, or by arrest for a term of up to six months, or by imprisonment for a term of up to two years with deprivation of the right to hold certain positions or engage in certain activities for a term of up to three years or without it.” If the citizen who was driving at the time of the traffic accident was drunk, then the prison sentence increases to 4 years . In the event of the death of the victim, the culprit, according to Part 3 of Art. 264 of the Criminal Code: “... is punishable by forced labor for a term of up to four years with deprivation of the right to hold certain positions or engage in certain activities for a term of up to three years, or imprisonment for a term of up to five years with deprivation of the right to hold certain positions or engage in certain activities for a term of up to three years".
Who is responsible for the accident: the owner or the driver
Russian legislation in terms of prosecution for offenses is based on the principle of the presumption of innocence. This means that a citizen must be held accountable only for those offenses for which guilt has been proven. This is stated in section 1.5 (part 1) of the Code of Administrative Offenses: “A person is subject to administrative liability only for those administrative offenses for which his guilt has been established.” Consequently, if the fault of the citizen who was driving the vehicle at the time of the collision is proven in the incident, then this citizen is responsible for the accident. It does not matter whether this person is the owner of the vehicle, a driver authorized to drive it, or a person who has taken possession of the vehicle without the knowledge of the owner. The owner of the car is not liable for an accident committed by another person.
What happens if you get into an accident without a license?
If a citizen, while driving a car without a driver's license (VL), becomes a participant in a road incident, then the extent of responsibility will depend on whether he is the guilty party or the victim. Let's consider both options.
- A citizen without rights is an injured party. In this case, he will be charged under Ch. 12.3 (part 2) of the Administrative Code: “Driving a vehicle by a driver who does not have documents with him for the right to drive it ... entails a warning or the imposition of an administrative fine in the amount of five hundred rubles.” A fine of up to 15,000 rubles if the citizen does not have a driver’s license in principle (Article 12.7, Part 1 of the Administrative Code). The consequences of an accident with an expired license are a fine of up to 30,000 rubles, and also if the person was previously deprived of a driver’s license (Article 12.7, Part 2 of the Administrative Code).
- Cause of an accident without a license. This scenario involves imputation of guilt according to the following legal norms:
- compensation for damage (Article 1064 of the Civil Code);
- administrative liability for violation of traffic rules resulting in a collision (Chapter 12 of the Administrative Code);
- criminal punishment if serious damage to health is caused or in the event of the death of the victim (Article 264 of the Criminal Code);
- penalties described in the previous paragraph for the injured driver.
Deprivation of rights for an accident
Deprivation of a driver's license from a citizen guilty of an accident is an administrative measure that makes it possible to punish the guilty person for an offense without limiting his freedom. In what cases are rights deprived? Confiscation of a driving license is possible for the following violations that caused a traffic incident:
- driving a vehicle while drunk;
- driving towards cars moving on a one-way road;
- speeding by more than 60 km/h;
- failure to give way to vehicles with special signals.
All of the above situations are described in Chapter. 12 Code of Administrative Offences. In addition to the above reasons, driving license can also be deprived in the event of an accident for repeated failure to comply with traffic rules, the primary violation of which is punishable only by an administrative fine.
What can happen to the person at fault in an accident? What types of liability can be applied and their features.
No driver is insured against road accidents, regardless of driving experience and knowledge of traffic rules. Depending on the type of offense, the culprit may face liability:
- Civil – compensation for material and moral damage caused, in accordance with the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
- Administrative – execution of punishment in accordance with the Administrative Code of the Russian Federation.
- Criminal – execution of punishment in accordance with the Criminal Law of the Russian Federation.
The choice of punishment depends on the specific features of the case.
○ Civil liability.
This type of responsibility includes:
- Compensation for damage caused to the vehicle.
- Financial resources paid by the culprit to the injured party during the period when the latter is unable to perform work.
- Compensation for moral damage.
- According to paragraph 1 of Art. 1064 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, damage caused to the property or person of a citizen, as well as to the property of a legal entity, must be fully compensated by the guilty party.
The culprit is the owner of the car, thus, if the vehicle belongs to an organization and its employee was driving, civil liability measures apply specifically to the legal entity.
An important point in resolving the conflict between the parties is the availability of insurance and its type.
- If the culprit has compulsory motor liability insurance, he can count on compensation for the damage caused to the injured party, but he will have to repair his own car himself. If there is no insurance, the culprit will have to pay compensation from his own funds, which can cause certain difficulties and delays.
- The CASCO policy, being a voluntary form of insurance, unlike compulsory motor liability insurance, provides full compensation for damage in the event of an accident. If you have it, you can count on receiving money not only for the injured party, but also for repairing your own vehicle. In the absence of such repairs, repairs are also paid for by the culprit himself.
Thus, the culprit can compensate for the damage caused:
- According to the MTPL policy.
- According to the CASCO policy.
- From own funds, by court decision.
○ Administrative responsibility.
This type of liability applies if harm to the health of the injured party is mild or moderate. The degree of punishment is determined on the basis of the relevant paragraphs of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, based on the specific situation.
- In case of mild harm to health, the culprit is given a fine in the amount of 2000 to 5000 rubles or deprivation of rights from 1 to 1.5 years (paragraph 2, clause 1, article 12.24 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
- If the harm to health is determined to be average, a fine of 10,000 to 25,000 rubles or deprivation of rights for a period of 1.5 to 2 years may be imposed (paragraph 2, paragraph 2, article 12.24 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
What exact fine will be assigned for an accident depends on the specific features of the case.
Most often, accidents occur due to violation of the following rules:
- Prohibition on the use of telephones while driving a vehicle (Article 12.36.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
- Turning on the turn signal when changing the trajectory of movement (Article 12.14 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
- Maintaining distance on the road (Part 1 of Article 12.15 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
- According to Article 4.6 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, a person who has been imposed an administrative penalty for committing an administrative offense is considered subject to this punishment within one year from the date of completion of the execution of the decision on the imposition of an administrative penalty.
- Repeated commission of a homogeneous administrative offense, if for committing the first administrative offense the person has already been subjected to an administrative penalty for which the period provided for in Article 4.6 of the Code of Administrative Offenses has not expired, is recognized as a circumstance aggravating administrative liability. (Article 4.3. Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation)
Administrative liability for the culprit of an accident can be applied in the form of:
- Warnings - executed by the judge, body, official who made the decision, by delivering or sending a copy of the decision.
- Imposition of an administrative fine - executed by the official who made the decision by delivering a protocol.
- Revocation of driver's license by court order.
Bringing to administrative liability is carried out by drawing up a protocol on the offense, drawn up in the presence of the offender.
○ Criminal liability.
In the event of the death of a victim in an accident, as well as the infliction of serious harm to his health, criminal liability is applied to the culprit in accordance with the relevant provisions of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
The degree of responsibility is determined by the court taking into account all the circumstances of the case (aggravating or mitigating) proven during the trial.
- According to Part 1 of Article 264 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, the culprit of an accident for unintentionally causing grievous bodily harm faces from 6 to 36 months of imprisonment or correctional labor for up to 2 years. An additional measure of deprivation of rights for up to 3 years is also applied.
If the result of an accident is the death of the victim, the punishment for the culprit is increased:
- If one person died, the term of correctional labor increases to 4 years, and imprisonment - to 5. If the culprit was drunk, the penalty is imprisonment for 7 years.
- If the number of deaths is more than one, the term of correctional labor increases to 5 years, imprisonment - to 7 years. If there are signs of intoxication, each penalty is increased by another 2 years.
If the result of an accident is regulated by the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, the investigation is conducted by the investigative authorities, after which the case is considered in court. It should be noted that in addition to the penalty applied, the culprit must also compensate for material damage to the injured party.
○ On-site proceedings.
According to the new rules for registering an accident, its participants have the opportunity to deal with the situation on their own, without contacting the police or the insurance company.
Reluctance to involve third parties in solving a problem may be due to:
- Minor damage to the vehicle, when it is easier to pay a small amount for repairs instead of waiting for an insurance payment.
- The reluctance of the culprit to increase the cost of his compulsory motor liability insurance, which increases with each payment by 1.6 times.
- Lack of time and desire to visit the traffic police and the insurance company.
In any of these cases, the culprit of the accident can simply transfer cash to the injured party and, with mutual agreement, end the conflict there. But do not forget about the possible risks of such behavior. For example, the injured party, after waiting for the culprit to leave, can call the traffic police and record the fact of an accident. To protect yourself from such developments, you should draw up a receipt for the transfer of money for car repairs. The document is filled out by hand indicating all the information about the participants in the incident and describing the nature of the damage. The information should be specified as accurately as possible, and a phrase stating that there are no claims against the culprit should be written down. The receipt will have legal force if signed by each party.
According to clause 26 of the traffic rules, participants in an accident can resolve the issue on their own if:
- Only the car was damaged, there were no casualties.
- There is no disagreement regarding the characteristics of the damage and the determination of the guilty party.
- Each party agrees not to file any paperwork related to the accident.
Another opportunity to independently register an accident is to draw up a Europrotocol. In addition to the conditions listed above, the following are mandatory for its execution:
- The fact of a collision of vehicles, their number should not exceed two.
- Each participant in an accident has a compulsory motor liability insurance policy (or a foreign equivalent “Green Card”).
A Europrotocol is drawn up on a special insurance notification form, according to which you can subsequently receive compensation without a long wait for specialists at the scene of the incident.
○ Advice from a lawyer:
✔ Does the insurance company compensate for the damage to the culprit?
Much depends on the type of insurance. If it is CASCO, then compensation will be paid in full, even if the client himself is to blame for the incident, provided that this is specified in the contract. As for compulsory motor liability insurance, there is no direct provision for payments to the guilty party, but they can be achieved by sending a claim to the insurance company or filing a lawsuit. It should be taken into account that the MTPL policy limits the amount of payment. Its limit in 2017 is 400 thousand if damage is caused to property, and if harm is caused to life and health - 500 thousand. The remaining amount of damage must be paid by the culprit himself.
✔ Does the guilty person compensate for non-material damage and in what amount?
This issue can be resolved both pre-trial and in court. However, cases when the culprit voluntarily compensates for moral damage are extremely rare, so, most likely, you will have to go to court. The amount of compensation is determined solely on the basis of fairness and reasonableness, there are no other criteria. In this case, a claim for compensation for moral damage is filed together with a claim for compensation for material damage and is considered by the court in the general manner.
Criminal liability of the driver who caused the accident. Lawyer Anatoly Antonov tells.
Published by: Vadim Kalyuzhny , specialist of the TopYurist.RU portal
3 types of liability in case of an accident
The most dangerous situation that can happen on the road is a traffic accident. Traffic regulations were created precisely to prevent such situations. In the article, we will consider what type of liability the driver will face as a result of causing an accident, as well as what fine for an accident is provided for in 2017.
According to the law, liability is divided into three types.
Civil (material) liability in case of an accident
This type obliges the culprit of the road accident to fully compensate for the damage caused to the victim.
In some situations, when, for example, as a result of an incident, the victim missed benefits or lost earnings, the culprit also pays compensation for this.
In order for the rights of victims to be protected from harm caused to their property, health or life during the use of a vehicle by other persons, a federal law was established.
Its essence lies in compulsory civil liability insurance of drivers and car owners - OSAGO.
Before driving a car, the driver must obtain liability insurance. This law solved the problem of compensation for damage after an accident to a significant extent.
However, there are circumstances in which the insurance company first pays the victim, but then has the right to demand compensation from the culprit for these losses.
Such circumstances include:
- escape of the culprit from the scene;
- the state of intoxication of the person responsible for the road accident;
- lack of a driver's license;
- intentionally caused accident.
Administrative liability in case of an accident
Such liability applies to the culprit of a road accident in cases where the emergency did not cause any bodily injury to the victim or his death.
For creating an emergency situation on the road, administrative fines are divided into types:
- deprivation of the driver's driving license for a period of up to 3 years;
- administrative arrest for a period of up to 15 days;
- up to 200 hours of community service;
- payment of an administrative fine.
Administrative fines can be paid in the amount of half of the amount no later than within 20 days after the decision was made. Otherwise, the fine for an accident must be paid in full.
Criminal liability in case of an accident
Criminal liability for an accident faces the culprit if the victim suffered particularly severe health damage as a result of the accident, or his death occurred. The type of criminal punishment for an accident depends on the number of injured people, as well as on the condition of the driver himself.
For example, if at the time of the accident the culprit was in a state of alcohol or other type of intoxication, then this circumstance will be an aggravating one. The culprit may face forced labor for a period of up to 5 years, as well as restriction of freedom for a period of up to 3 years, or imprisonment for up to 9 years in time.
Additionally, penalties may be accompanied by a ban on holding certain groups of positions or working in certain areas for a period of up to 3 years.
Fines for road accidents
In the Russian Federation, the following fines are provided for violation of traffic rules during an accident by the culprit of the accident:
- If a driver violates traffic rules by leaving the scene of a traffic accident in which he was a participant, then he faces arrest for a period of up to 15 days or deprivation of his license for a period of 12 to 15 months.
- If a driver who did not display the appropriate sign during an accident moved the car from the scene of the accident or did not comply with any other requirements stipulated by the traffic rules, then he will have to pay a fine of up to 1000 rubles.
The following violations can also lead to an accident:
- driving a vehicle if it has any malfunctions or conditions that result in a risk of violating road safety, of which the driver knew in advance, is punishable by a warning or a fine of 500 rubles;
- a driver who knowingly drives a car with a breakdown in the brake system (the parking brake does not engage) or in the steering will have to pay 500 rubles. Sometimes the punishment consists of suspension from driving the vehicle, or even detention of the vehicle;
- If the driver or the passengers he is carrying are not wearing seat belts, the fine will be 1,000 rubles. This also includes driving and transporting a motorcycle without special helmets or wearing unfastened helmets;
- A driver who drives a vehicle while intoxicated is subject to a fine of 30,000 rubles with an additional deprivation of driving privileges for 1.5–2 years. The vehicle is detained. The same penalty is provided for handing over a car to a person who is intoxicated;
- If the driver is intoxicated and does not have a license to drive a vehicle, or has previously lost these rights, then a penalty of arrest for 10–15 days is provided. Drivers who are not subject to arrest are fined 30,000 rubles. The vehicle is detained;
- for driving on pedestrian and/or bicycle paths, sidewalks, a penalty of 2,000 rubles is provided;
- for driving a vehicle on oncoming roads where one-way traffic is provided, the driver will be punished with fines in the amount of 5,000 rubles and/or deprivation of driving privileges for 4–6 months;
- for using a mobile phone while driving, if it is not equipped with special technical equipment. devices for hands-free conversations, the driver will have to pay 1,500 rubles;
- a driver who has crossed a traffic controller's prohibited gesture or a traffic light signal will have to pay a fine of 1,000 rubles. If such a violation is repeated, then the amount of payment increases to 5,000 rubles or the culprit is deprived of his rights for 4–6 months;
- if you did not stop in front of the stop line or at a traffic light signal, the fine will be 800 rubles;
- crossing during a traffic jam, thereby creating obstacles to general traffic, as well as going to an intersection, faces a fine of 1,000 rubles;
- stopping for non-compliance with markings and road signs - 1,500 rubles, as well as detaining the vehicle. In Moscow and St. Petersburg, the fine is larger - 3,000 rubles;
- The driver of a vehicle who parks 5 meters in front of or directly at a pedestrian crossing or on the sidewalk must pay a fine of 1,000 rubles. The vehicle is then detained;
- parking or stopping at a stop for public vehicles, as well as less than 15 meters from it, is punishable by 1000 rubles. fine and detention of the vehicle;
- parking or stopping on tram tracks - 1,500 rubles fine and detention of the car;
- if the stop/parking was made in a tunnel, or created obstacles to the general flow of traffic, a fine of 2,000 rubles is imposed, and the vehicle is also detained.
For failure to pay the fine within the allotted time, the driver faces paying it twice (at least 1,000 rubles), or compulsory work for up to 50 hours, or arrest for a period of up to 15 days.