How are wheels on cars marked?
Markings, parameters of wheels for passenger cars
Wheel rims are used on any modern vehicle: the quality of the car’s grip on the road depends on them, since it is on this part that the tire is put on. Discs differ not only in properties and quality, but also in size, so when choosing a product it is important to know what the disc marking means.
Most characteristics are more than just disk size: they also affect security. For specific car models, certain wheel models are provided; it is better to find out which ones in advance.
The marking is standard for all types of products, no matter whether they are made of steel, aluminum, cast or stamped. All designations will be standard, made in accordance with the UN/ECE 124 certification adopted by the European Union.
The width of the rim can be indicated (rim width), followed by a number. It is indicated in inches and indicates the distance between the edges of the rim located on the inside. This is important when purchasing tires, as the tire is designed to fit a specific rim width. Ideally, the value will be in the middle range of the selected tire.
The lip type is designated by the letter J. This parameter indicates what shape the edge of the rim has. The junction of the disk and tire for passenger cars may be indicated by other letters. Each letter is a different edge shape: P, JK, K, D, JJ, B, J. Using the letters you can learn the following:
- Curvature radius.
- The angle of inclination of the shelves, their height.
- What contour shape does the profile have?
J is the most common standard for passenger cars; for models with all-wheel drive, the JJ type is more often used.
Not only the installation method, but also how heavy the loads will have to be used when balancing the wheels depends on the shape of the rim flanges. Externally, the models are similar, but the manufacturer indicates which one is suitable for your car, as this affects driving stability.
Connectivity
The marking of wheel rims with the letter “X” means that this is a non-separable structure cast from metal; there may be a “-“ sign; on the contrary, it indicates that the structure can be disassembled and is assembled from several parts. A non-separable disc is lighter, has higher strength, it is used with elastic rubber, and is most often installed on passenger vehicles. For trucks, where the tires are more rigid, collapsible structures are used, since mounting the tire on another disc will be impossible.
Mounting diameter
This parameter can be indicated by the words (rim diameter); deciphering the disk markings in this case will also not cause difficulties. This indicator means the size of the landing rim calculated for the tire. Simply put, this is what is indicated by the letter R, followed by a number, for example, 16.
Hump rings
When choosing wheels for a car, it is necessary to take into account the designations of wheel rims. Hump is designated by the Latin letter H. The following options are found:
- H – ring protrusions are available on one side only.
- H2 – there are annular projections on both sides of the disk. This design is needed if tubeless tires are installed.
- FH (Flat Hump) means that the shape of the hump will be flat.
- AH – asymmetric protrusion.
Mounting holes
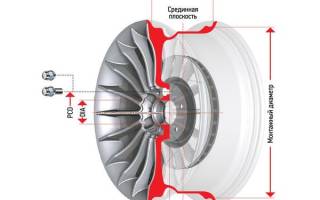
The PCD marking may contain different numbers, for example, 4x100: this means that there are 4 holes, and 100 is the diameter of the circle with all the holes for fasteners placed on it. The number of holes for different machines is different, from 4 to 6. The diameter of the circle has standard values - 98 ÷ 139.7.
It is not always possible to determine by eye the correspondence between the size of the hub and the disk, and installing a 98 disk instead of 100 can lead to misalignment of the wheel, which will cause runout, as well as spontaneous unscrewing of the bolts.
Disc offset
Denoted by the letters ET: this distance indicates the gap between the plane relative to the center of the cross section of the disk and the wheel hub. This value is indicated in millimeters. Don’t be surprised if you see a minus in front of the number - the offset can be negative.
To prevent the disk from breaking under load, you should choose exactly the one specified by the manufacturer.
Bore Diameter (DIA)
This disc designation parameter is measured in millimeters and is designated by the letter d. It shows the diameter of the central hole for the car's hub. For passenger cars, this is most often 50-70 mm; the product is selected exactly to size, otherwise the disc either will not fit or will dangle, which will lead to tragic consequences.
Where is the disc marking located?
Now that it has become clear which letters and numbers mean what, one question remains - where is the marking of alloy wheels located. For any element, regardless of what technology it is made of and what material it is made of, marking is provided. It is not difficult to find, since it is located on the front side and is standardly located in the same place for all disks. The only difference is that the markings can be on both the outside and the inside; the latter is more common, since it does not spoil the appearance of the claim. Pay attention to the front of the product. For different models, the data may be extruded in slightly different places, but basically you will see information in the free spaces between the holes for the bolts for attaching the disc to the car's hub. On some models, the information may be on the front side of the rim. Most often, such markings are found on disks made in Ukraine and products of some European companies.
Deciphering disk parameters is an important skill that will be useful to a motorist when choosing a product for his iron horse. It is worth noting that the disc, unlike rubber, is not a seasonal product, so it is used at any time of the year; nothing special is provided for winter. In addition, when choosing, always check the manufacturer's technical requirements. Usually several types of disks are suitable, but you cannot deviate from the sizes and parameters specified by the manufacturer.
Decoding the markings of passenger car wheels
Any wheel rim is an important part of the car, connecting it to the road surface through the tire. If the latter wears out, it becomes necessary to purchase new tires, and for this you should know the basic parameters of the disk itself, because this information is not limited only to the number of bolt holes and rim diameter, which are what car enthusiasts most often pay attention to. At the same time, most of the parameters that are not taken into account are very significant for driving safety, as well as the safety of the suspension. Therefore, next we will try to understand in more detail the key characteristics of rims.
Let's look at an example of disk marking
First of all, when buying wheels, you need to know which models are allowed for installation on a particular car, and then study the information about the parameters of the samples you like. The ability to read the applied markings, which are standard for wheels (cast and stamped) produced in the class of light-duty vehicles, will help with this. The marking is applied in accordance with the UN/ECE124 regulation in all EU countries, and looks approximately as follows:
7.5 J x 15 H2 5x100 ET40 d54.1
We will decipher this example further.
Rim Width
“7.5” is the mounting width or distance between the edges of the disk, measured in inches. Converted to the metric system, it turns out 7.5 * 25.4 = 190.5 millimeters. It should be noted that each tire has a certain range of permissible (recommended) rim width. The optimal width will be closest to the middle of the specified range. Otherwise, problems with beading of tires may arise, and its characteristics will deteriorate.
Flange (edge type)
The letter “J” (may be found: P, D, B, K, JK, JJ, J) contains information about the flange of the rim, which indicates information about the height and inclination of the flanges, the radius of curvature, the design and shape of the profile . The most common flange types today are "J" and "JJ". The first are intended for single-wheel drive cars, the second - for all-wheel drive. The type of flange determines the installation of the tire, resistance to displacement in an emergency situation, as well as the mass of compensating weights. In any case, it is optimal that this parameter coincides with that recommended by the car manufacturer.
Detachable rim
The symbol “x” indicates the one-piece (monolithic) type of the wheel rim. Otherwise, the disk is marked with a “-” sign, which indicates the presence of several components for which it can be disassembled if necessary. Note that one-piece structures are more rigid and lightweight compared to collapsible ones.
The “x” marking also indicates that these wheels are intended to be equipped with elastic tires, which are used on passenger cars and light trucks. Rubber for large trucks is rigid and requires discs of a composite design for installation, otherwise mounting on the rim becomes impossible.
Rim Diameter (mounting diameter)
The next number “15” is an indicator of the parameters of the landing rim for tires, calculated in inches. This size is often also called the radius of the disk. In the process of selecting and purchasing a tire, you must ensure that this parameter absolutely matches the corresponding tire size. Note that the range of diameters under consideration for ordinary (standard) passenger cars and SUVs ranges from 13-21 inches.
Hump (rolls and protrusions)
The so-called “humps” (H2), or otherwise annular protrusions, are located on both sides of the disk, and are intended for fixing tubeless-type automobile tires on it. Rolls prevent the outflow of air from under a tubeless tire when exposed to external influences. In addition to the example and considered case with “H2” with a double-sided arrangement, there are tackles of the following types:
- H - on the only side of the disk.
- FH (Flat Hump) - with a flat shape.
- AH (Asymmetric Hump) - with an asymmetrical protrusion.
Pitch Circle Diameter, PCD (mounting holes)
In this case, the designation “5x100” indicates the location of the disk holes intended for fastening it to the car axle. The values "5" and "100" indicate the number of these holes and the diameter of the circle of their location, respectively. For passenger vehicles, the number of these holes can vary from 4 to 6, while the standard circumference diameters for their location are in the range of 98 - 139.7 millimeters. It should be remembered that it is not always possible to determine “by eye” the correspondence between the parameters of the disk and the hub, and an incorrect selection can provoke a misalignment of the wheel, which will lead to loosening of the bolts or runout.
Einpress Tief, ET (disc offset)
The designation “ET40” in this case defines the disc offset, which is the distance between two planes passing through the contact surface of the hub with the disc and through the cross-section center of the disc itself (transverse), respectively. This distance is measured in millimeters. At the same time, the offset can be both positive and negative (ET40, as in our case, or for example ET-25). To avoid the occurrence of emergency situations caused by external forces and capable of destroying the disc and damaging the suspension, the offset indicator must be selected in full accordance with the recommendations of the manufacturer of a particular car brand.
Hub Diameter, DIA (landing diameter)
Marker “d54.1” is the diameter of the central hole of the wheel rim, otherwise called the landing or hub. It is indicated in millimeters, and for passenger vehicles ranges from 50-70 mm. This parameter is very important, and therefore must fully correspond to the belt of the car hub.
In conclusion, it must be said that each of the considered parameters of a car rim is important, and even with the slightest deviation from the requirements, there may be a threat of intense tire wear, which entails the risk of complete destruction of the rubber in an extreme situation, be it a sharp turn or high speed . For this reason, the wheels of a personal car must be kept in perfect condition and checked before each trip.
Wheels - types, markings
Disk types
Wheels are divided into two large groups: steel and made of light alloys.
1. Steel wheels
2. Alloy wheels
Steel disks , or more precisely, their parts, are stamped from a sheet, and then these parts are joined by welding. It turns out to be extremely cheap and quite high quality - which is why the vast majority of cars on the factory assembly line are equipped with steel ones.
+ low price;
+ quite high strength and the ability to recover even in the event of very strong crushing of the edges.
- large mass;
— low manufacturing accuracy (which means there may be problems with balancing) and outdated design;
- low corrosion resistance, largely due to the quality of the coating. At the same time, the lowest corrosion resistance is found in discs coated with enamel and electrophoresis.
Alloy wheels are superior to steel wheels in many ways. They allow any design play, they have the highest manufacturing precision, they perfectly remove heat from the brake unit, but most importantly, they are light (the lighter the discs, the lower the total mass of the unsprung parts of the car, which means the better). These are general advantages. It is possible to accurately judge their pros and cons only by taking into account how they are made and from what particular alloy - there are many nuances here, every wheel is different.
According to the manufacturing method, light alloy wheels are divided into cast and forged.
A cast disc has a granular internal structure of the metal, and this is its main disadvantage: when driving for a long time over potholes, the metal begins to accumulate microcracks (invisible and therefore dangerous), which will sooner or later manifest themselves - the disc can crack from a strong impact.
— a cast disc requires serious surface protection; without this, it quickly becomes covered with a whitish oxide film and loses its presentation;
— the cast disc is quite fragile: with a very strong impact it splits, which is extremely dangerous at high speed. To ensure sufficient mechanical strength, the wall thickness has to be increased, and this reduces the much-desired weight gain.
Forged disc .
Forging provides exceptionally high strength and rigidity of the structure. The forged disc withstands the strongest impacts; in extreme cases, it does not burst like a cast one, but bends without cracking, which is certainly safer. In addition, it is very lightweight. Compare: a stamped steel disk, for example, for the 7th BMW model weighs 9 kg, cast aluminum - 7.8 kg, and forged aluminum - 6.8 kg. It is theoretically possible to dent it, but the suspension will more likely fall apart than the edge of a forged wheel will dent. The corrosion resistance of a forged disc is significantly higher than that of a cast disc, which means that the requirements for surface protection are lower.
If it were not for the high cost due to the complexity of the technology, forged wheels would probably have supplanted all others long ago - for most characteristics, forged wheels have no equal. Discs are cast and forged from aluminum and magnesium alloys. If you arrange alloy wheels in order “from minus to plus” based on purely technical parameters, then the row will be as follows: cast magnesium (light, but capricious, cracks quickly), cast aluminum (normal in terms of the totality of qualities), forged aluminum (durable and lightweight) and forged magnesium (super strong and lightweight). But when choosing disks, it is clear that not only technical parameters play a role. We advise you to immediately discard extremes: magnesium wheels, both cast and forged, are very rare; as a rule, they are made only to order for sports cars.
Disc markings.
The disk should indicate:
— Trademark or name of the manufacturer.
— Date of manufacture.
Usually a year and a week. For example: 0407 means the disc was released in the 4th week of 2007. — Wheel offset (some American companies for some reason ignore this requirement; Europeans always indicate the offset).
– SAE, ISO, TUV – mark of the regulatory body.
The marking indicates that the wheels comply with international rules or standards (in Russian, OTK; many companies brand their products not with dry alphanumeric indices, but with birds, flowers and other art). — A separate X-ray inspection stamp (usually for cast ones, indicating the absence of internal defects - shells).
– MAX LOAD 2000LB - a very common designation for the maximum load on a wheel (indicated in kilograms or pounds). For example, the maximum load is 2000 lbs (908kg).
In addition, the disk may indicate:
— PCD 100/4 – connecting dimensions;
— MAX PSI 50 COLD - means that for a given rim the tire pressure should not exceed 50 feet per square inch (3.5 kgf/sq.cm).
The word COLD reminds you that the tire pressure should be measured when the tire is cold. — Melt number.
— Method of production. If the disc is forged - FORGED. This inscription is not provided for by any standards; it is stamped on the disk solely for prestige.
The full size, by which a specialist or you yourself can understand whether a given disc is suitable for a particular car. The wheel rim layout is as follows: 6.5JxR15 ET33 4*98 D58.1 .
6.5 is the rim width in inches.
Standard range: 3.5; 4.0; 4.5; 5.0; 5.5; 6.0; 6.5 and 7.0 inches; Tuning, sports and off-road cars may have wider wheels. The use of both too wide and too narrow rims (relative to the width of the tire profile) is undesirable: the design profile of the tire is violated (the sidewalls are either compressed by the edges of the rim or stretched on it), due to which its driving characteristics deteriorate - response to turning, resistance to slip , lateral stiffness. The permissible deviation of the rim width from the norm is 0.5-1.0 inches for discs with a mounting diameter of up to 14 inches; and 1.0-1.5 inches - for disks with a diameter of 15 inches or more. But it’s better, of course, to take the disk exactly under the tire.
J - deciphering these symbols is quite difficult. These symbols are service symbols; they are important not for the consumer, but for the manufacturer and seller. We will briefly touch on them only because, when included in the dimensional inscription, they attract the buyer’s attention and raise a lot of questions. Decryption - in catalogs. J - encoded information about the design features of the side flanges of the rim (angles of inclination, radii, roundings, etc.). Depending on the specific design, it may be written JJ, JK, K or L. H2 is encoded information about the shape of the annular projections (humps) on the rim flanges that keep the tubeless tire from jumping off the rim. There are many designs of humps. There is a simple Hump H (Hump), double H2, flat FH (Flat Hump), asymmetrical AH (Asymmetric Hump), combined CH (Combi Hump). Sometimes they do without humps; a special shelf SL (Special Ledge) is made on the rim, the parameters of which are adjusted so that the tire holds securely, without “clinging” to anything other than the edge of the rim.
15 is the mounting diameter of the rim in inches. Standard range for cars and SUVs: 10, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18 and 19 inches.
ET33 - wheel offset in millimeters. May be designated as OFFSET or DEPORT. This is the distance between the longitudinal plane of symmetry of the rim and the mounting (fitting) plane of the wheel. The offset can be zero, positive (the disc hub protrudes outward relative to the middle of the rim) and negative (the hub is recessed). For each car model, the offset is calculated so as to ensure optimal stability and controllability of the car, as well as the least load on the wheel bearings. The Germans designate the offset ET (for example, ET30 (mm), if its value is positive, or ET-30, if negative), the French - DEPORT, manufacturers from other countries usually use the English OFFSET.
Installing wheels with abnormal offset on a car:
— reducing the offset makes the wheel track wider; Although this slightly increases the stability of the car and gives it a “stylish racing look,” it also dramatically overloads the wheel bearings and suspension.
— increase in reach, i.e. narrowing the track is, as a rule, impossible - the disc will rest against the brake mechanisms.
To install “non-original” disks with incorrect offset (but correct drilling), it is necessary to have a spacer between the mating plane of the disk and the hub - to correct the offset.
4*98 - PCD (Pitch Circle Diameter). Number 4 is the number of mounting holes for bolts or nuts. The wheel mounting holes are located at different diameters with tight positional tolerances relative to the central hole.
Since the mounting holes are made with a significant tolerance plus in diameter, you can make a mistake in choosing a PCD if it differs from the standard one by a couple of millimeters.
For example, a PCD98/4 wheel is often put on a hub with PCD100/4 (98 mm from 100 cannot be distinguished by eye). It is unacceptable. In this case, of all the nuts (or bolts), only one will be fully tightened; the remaining holes will “lead away” and the fasteners will remain untightened or tightened skewed - the fit of the wheel on the hub will be incomplete. While driving, such a wheel will “beat”, in addition, not fully tightened nuts will unscrew by themselves.
If necessary, the PCD can be calculated by measuring the distance between the centers of adjacent holes (S). This can be done with a regular ruler without removing the wheels from the car.
For discs with three mounting bolts (or nuts), to obtain the PCD value, the distance S must be divided by a factor of 0.8658.
Wheel rim markings, step by step explanation
Publication date: December 16, 2015.
Category: Automotive equipment.
Every car enthusiast strives to equip his iron horse with only the best. These include leather seat covers, expensive sound, navigation systems and much more. But for some reason, when you need to purchase new rims, most drivers are guided only by the fact that the products can be either stamped or cast. Meanwhile, there are other parameters of car wheels, on which not only the safety of movement on the roadway, but the durability of the suspension depends.
If you notice that the tires wear out too quickly, the car does not listen and accelerates poorly, then most likely the problem is not in the tires themselves, but in the fact that when choosing wheels for the car, you chose the wrong model. To prevent this from happening, let's figure out what kind of decoding of wheel rims exists today. By the way, the marking must be standard; for example, in Europe there are strict rules and regulations, so discs are certified according to UN/ECE 124.
Standard marking of a car wheel
The parameters of wheel rims, which will not take much time to decipher, are abbreviations that are the same all over the world for cast or forged wheels. There are also no divisions by type of car as such, since the marking is the same for all vehicles.
In order to quickly understand the notations, let's look at them using an example: 7.5 J x 16 H2 4x98 ET45 d54.1. Based on this information, we can see the following markings.
Rim width
The first number is responsible for this parameter - 7.5, indicating the distance between the inner edges of the rim. The fact is that each tire has a certain rim width range, which is measured in inches. Therefore, it is better to select wheels whose rim width is approximately in the middle of this range.
Rim edge type
In this case, the letter J tells us about the type of edge - the designation of the shape of the edge of the rim. This is where the disc connects to the tire. The following letter combinations may also occur: JJ, JK, K, B, D, P. It is difficult to say exactly what profile each of these letters represents, since in European standards the description of all these combinations is very large and rather ambiguous. Each symbol may indicate the shape or radius of the contour, and in some situations it may indicate the angle of inclination of the rim flanges. Therefore, we will consider only the most popular and well-known. JJ indicates that this is an SUV wheel. If the letter K is written, then this is the best option for a Jaguar car, and P and B are most often installed on Volkswagen Beetles. If we talk about trucks, then the following group of letter symbols is responsible for this category: E, F, G, H.
Rim connector
The X symbol means that in this case the rim is one-piece, that is, it is a single part. But if you notice the “-” sign, then this is a model consisting of several parts, thanks to which it can be disassembled and reassembled. One-piece discs are considered the best, since in this case their design is much lighter and more rigid. Another advantage of one-piece models is the ability to install elastic tires on them. If we are talking about hard tires, which are most often equipped with trucks, then preference should be given, on the contrary, to split rims, otherwise you simply will not be able to install the tire on the rim.
Mounting diameter
Continuing to look at the parameters of the wheels on the car, we see the number 16, which is responsible for the mounting diameter of the wheel rim, corresponding to the mounting size of the tire. The rim flange is not considered in this case. Therefore, there are standard values for this parameter from 10 to 19 inches.
Ring projections (rolls)
In the example, H2 means that in this case we have a certain type of structure, consisting of humps located on both sides, which are designed for more reliable fixation of tubeless tires. In this case, there is no outflow of air (in the case of lateral impact on the tire). In a situation where there is an H mark on the disk, this will mean that the hump is located on only one side. The following letter variations also exist:
- FH – flat hump;
- AH – asymmetrical;
- CH – combined;
- SL – there are no humps in the design (in this case the tire will hold on to the edges of the rim).
Location of mounting holes
This parameter is indicated by the symbols 4x98, where the first number tells us the number of mounting holes, and the number 98 is the diameter of the circle itself, the center of which is located in the same place as the center of the disk. Usually the number of such holes is from 4 to 6, although sometimes you can find models with 3, 8, 10 pieces.
The standard value for the circle diameter can be in the range from 98 to 139.7.
When choosing disks based on this parameter, many car enthusiasts make one common mistake - they try to determine by eye the size of the hub and the disk. As a result, having installed a 98 disc instead of a 100, they are faced with the fact that the wheels are simply warped. As a result, the bolts begin to unscrew spontaneously.
Disc offset
ET45 in our example is a value indicating the distance between the plane that passes through the center of the cross section of the disk and the plane located in the contact zone between the disk and the hub.
Disc failure occurs:
- Positive when the plane of symmetry of the car disk is located further from the center of the car, compared to the mating plane;
- Negative when, on the contrary, the mating plane is located further from the center of the machine than the plane of symmetry of the disk. Then the marking would look like ET-45;
- Zero (ET0), when the center of symmetry of the disk coincides with the mating plane.
Before choosing a disc, it is better to study the recommendations of the car manufacturer. Which should indicate in the relevant documents for the car which type of disc offset is suitable for your car model.
Bore hole diameter
d54.1 corresponds to the diameter of the central hole of the disk (measured in millimeters). The standard range for this parameter is from 50 to 70 mm for passenger cars. It is very important to select a disk that will exactly match this parameter and the size of the seating belt located on the machine hub. If it turns out that the diameter was chosen smaller, then you simply will not be able to put on the disc.
There are also additional markings on car rims, the decoding of which will be useful.
Additional markings
In addition to standard designations, when choosing disks you may come across the following abbreviations:
- MAX LOAD – a parameter that shows what maximum load is allowed on the disks;
- MAX PSI 50 COLD - indicates that the tire pressure should not exceed 3.5 kgf/sq.cm. COLD is a reminder that the tire pressure should only be measured when the tire is cold;
- FORGET – indicates that the disc was made by forging;
- BEADLOCK – the disc is equipped with a tire locking device. It is prohibited to use such products;
- BEADLOCK SIMULATOR – states that the disk is equipped with a system that simulates a “beadlock”. This element is rather decorative in nature, so such models are no different from ordinary disks;
- SAE/ISO/TUV is a marking of a regulatory body indicating that products comply with international standards.
In addition, the disc may indicate the date of manufacture. The first two digits are the week, and the subsequent ones are the year. For example, 0510 means that the product left the assembly line in the 5th week of 2010.
In custody
You should not be negligent in the choice of wheel rims, since the safety of the driver, as well as the dynamism and controllability of the car, directly depend on these products. The parameters of VAZ wheel rims are no different from those listed above, because, as already mentioned, there are certain standards that are taken into account in our country. Therefore, when choosing disks, carefully read their markings to choose the best option.
What do the markings on rims say: explanation of symbols, overview of parameters, advice on selection
Wheels or disks, as they are commonly called in everyday life, with all their apparent simplicity, are a very important element on which traffic safety depends. To prevent the purchase of new wheels from turning into “Russian roulette” for car enthusiasts, almost all more or less significant parameters of automobile disk wheels are strictly regulated by standards. And one of the most important requirements of “wheel” standards around the world is the presence and content of markings. To understand its nuances, you need to know the rules for decoding factory designations.
What information is contained in the inscriptions on car rims?
Strictly speaking, the “discs” that we buy in auto parts stores are not actually discs at all, but wheels. And the “disc” marking is usually applied not to it, but to the wheel rim.
GOST R 52390–2005 “Disc wheels” defines a wheel as a rotating and load-transmitting unit (element) located between the tire and the hub. The wheel consists of two main parts: the rim and the central disk.
A careful study of the markings will help you not only make sure that this design has been tested and its use will be safe, but also understand whether the wheel is suitable for installation on your car.
How to decipher the markings
All disks, regardless of whether they are cast or stamped, have standard markings. In any case, the designation must contain:
- the Latin letter I or S, indicating whether the wheel is “identical” (I), that is, exactly the same as the wheels that were installed on production cars, or special (S), which was certified without being “linked” to any car . For elements that were included in the certified vehicle (original), the letter marking is not applied, but they may indicate the designation of the vehicle manufacturer and the spare parts catalog number;
- manufacturer's name or trademark;
- wheel rim profile designation;
- rim offset size in millimeters;
- date of manufacture (at least month and year);
- serial number (designation).
What do the numbers on the rim mean?
The rim marking consists of the following symbols:
- rim contour (shape of the side flange);
- nominal diameter (usually in inches);
- nominal width (also usually in inches);
- symbol of a one-piece rim (on all modern passenger cars the one-piece rim is the “x” sign).
Decoding the symbols on the wheels of a passenger car
For example, on the car disk we found the following entry: KrKZ UA 16 06 5 1 / 2 JxH2 ET47 560 226.15. We read:
- KrKZ - Kremenchug Wheel Plant;
- UA - Ukraine;
- 16 06 - June 2016;
- 5 1/2 - rim width 5.5 inches;
- J is the shape of the side flange of the rim. As a rule, rims with a diameter of 13 inches or more have a J flange shape, smaller ones - B;
- x—one-piece rim;
- H2 - design of the landing flanges: H means the presence of a special protrusion for the use of tubeless tires, 2 - that such a protrusion is made on both the outer and inner sides of the rim (if there is no number 2, then the protrusion H is only on the outer side of the rim) . For tubeless tires, in addition to the H lug design, there are wheels with the FH design.
- ET47 - rim offset 47 mm. Overhang is the distance that needs to be measured from the mating plane of the disk to the central plane of the rim;
- 560 - maximum static load on the wheel 560 kilograms;
- 226.15 - factory designation of the wheel.
In addition to the mandatory marking signs, the wheel is usually marked with a symbol for the mounting dimensions of the disks:
- LZ - number of mounting holes;
- PCD - hole location diameter;
- DIA is the diameter of the central hole.
Often the number of mounting holes is indicated along with the PCD in the form of 4x98, 5x112, etc.
We choose a wheel rim for a car according to all the rules
Even a novice driver understands that not every wheel fits a particular car. To choose a disk that is optimally suited for a particular machine, you need to carefully study its parameters. Let's look at the most important of them.
Vehicle manufacturer
Before starting sales, any wheel manufacturer is obliged to conduct tests, certify the model and thereby confirm the safety of using its design. Therefore, the name of the manufacturer does not necessarily have to be decisive when choosing a wheel. However, there may be nuances here. Therefore, before buying, it makes sense to read reviews on the Internet, perhaps talk with your neighbors in the parking lot if their cars have wheels from the same manufacturer. It happens that factory wheel caps fit loosely on the rim of another manufacturer, but dangle when driving. Accordingly, driving on new wheels with such caps is not recommended.
How to choose the rim width
Select the rim width from the range specified in the vehicle's owner's manual. A wider-than-permissible rim with a large tire can cause the wheels to hit the suspension or body parts. If not when turning with a large radius on a flat surface, then on an uneven road while moving in the wheel arch simultaneously with a turn.
If you already have tires, then you need to choose the width of the rim to match their width. Each tire width is associated with a number of rim sizes. If you choose the widest rim from this range, the tire's contact patch with the road will be wider, and it will cling to the road better. However, in this case, the tire will become easier to break through and press weaker against the edge of the rim, which is fraught with loss of tightness on uneven roads when the pressure in the tire is below normal.
On a narrow rim, the tire holds onto the edge of the rim more tightly, but at the same time its grip on the road is worse, and it “breaks” more easily under the influence of lateral forces in a turn. It should be understood that the differences we are talking about are minimal and practically unnoticeable during normal operation, since they are all within the limits allowed by the manufacturer.
What does the rim design affect?
When purchasing rim designs, experimentation is not appropriate, especially when using tubeless tires. We don't want the tire to fly off the rim at full speed. We select the rim in strict accordance with the manufacturer's instructions.
The main dimensions of the rim - its width and bore diameter - are selected in strict accordance with the tire parameters
Allowable disc overhang
The offset has a positive value when the rim is shifted from the mating plane into the vehicle. Often, tuning enthusiasts choose wheels with smaller offsets, even negative ones. They believe that this makes the car look “cooler” because the larger track makes it more stable when cornering. This is partly true, but you need to understand that car designers choose wheel offset for a reason.
The position of the middle plane of the rim relative to the steering axis of the wheel determines the “rolling shoulder” - a very important parameter in the context of car handling. By reducing the wheel offset, we increase the rolling shoulder, which increases the force on the steering wheel, the impact on the steering wheel when one wheel hits a bump, the load on the steering tips and the suspension.
The wheel hub is designed for a certain offset, so changing it in one direction or the other has a bad effect on the durability of the hub bearing. And just as in the case of a large tire width, the wheel may touch vehicle parts.
The wheel offset must strictly comply with the factory recommendations or be very close to it.
How to calculate the load capacity of a disk
We find the factory data plate on the car and look at it for the maximum permissible axle load. From these, we select the axle with the highest load and divide the load figure in half. This is the minimum wheel load capacity that is suitable for your vehicle. You can take a disk with a higher load, but it is unacceptable to use a lesser one. It’s also not worth purchasing a disk with a load capacity that significantly exceeds what you need, because it is heavier, which means it puts more stress on the chassis and increases fuel consumption. And, logically, it costs much more.
How to determine PCD diameter
The diameter of the holes for the mounting bolts in the disk must clearly correspond to the diameter in the hub. Even if the difference seems insignificant to you, do not neglect it. Perhaps, with a slight discrepancy, the bolts can be tightened without problems, but due to uneven pressure on the edge of the hole, they will weaken very quickly. Losing a wheel while driving is an inevitable accident and often with very serious consequences.
Why is it important to choose the correct DIA size?
The diameter of the central hole is no less important than the previous parameter. Almost all passenger car wheels are designed in such a way that the load from the wheel to the hub is transmitted through the central hole. The bolts serve to fix the wheel and transmit braking force and torque if the wheel is driven. Even a slight mismatch of diameters in the fit of the wheel on the hub will lead to wheel runout. The holes will become loose, the bolts will weaken, and again nothing good awaits us.
Video: how disks should be labeled and where to find out their parameters
To purchase wheels that are ideal for your car, you need to measure the diameter of the wheels and look at the markings on their rims. Remember that choosing a disk is always a matter of your safety. To feel calm and confident on the road, carefully read the markings and purchase wheels that match your car.